Page 1142 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 1142
Keratoconjunctivitis: Eosinophilic, Cats 568.e1
Keratoconjunctivitis: Eosinophilic, Cats Client Education
Sheet
VetBooks.ir Diseases and Disorders
• Many cats have a history of corneal ulceration
BASIC INFORMATION
and are positive for FHV on polymerase mainstay in its management. Primarily, topical
corticosteroids are essential to control clinical
Definition chain reaction (PCR) analysis. However, cats signs, and lifelong treatment is commonly
This proliferative condition in cats affects the rarely show recrudescence while being treated required at some level to prevent recurrence.
cornea, conjunctiva, or both. The severity varies with topical steroids.
between simple neovascularization and blinding Acute General Treatment
disease. Cytology is characteristic and reveals DIAGNOSIS • Topical prednisolone acetate 1% or topical
eosinophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and dexamethasone sodium phosphate 0.1%
variable mast cells. Diagnostic Overview q 6h, with tapering by 1 drop daily (or
A tentative diagnosis based on clinical signs can 25% reduction) q 1-2 weeks. The rate of
Synonyms be made in most cases of eosinophilic keratitis. taper is based on the therapeutic response
Eosinophilic keratitis (most commonly used as seen in the resolution of the corneal
term), keratoconjunctivitis, eosinophilic Differential Diagnosis plaque and disappearance of the corneal
conjunctivitis, proliferative feline eosinophilic • Chronic ulcerative keratitis (p. 209) vascularization
keratitis, proliferative keratoconjunctivitis • Herpesviral stromal keratitis (p. 464) • Concurrent antibiotic and/or antiviral
• Granulation tissue (p. 212) therapy may be added if corneal ulceration
Epidemiology • Corneal neoplasia (lymphoma is rare, is present or FHV type 1 involvement is
SPECIES, AGE, SEX corneal squamous cell carcinoma has not suspected.
Most commonly seen in younger adults (median been reported in cats)
age is 5-6 years). Chronic Treatment
Initial Database • After the eosinophilic keratitis is in remission,
GENETICS, BREED PREDISPOSITION • Complete ophthalmic exam (p. 1137) therapy is maintained with topical steroids
No breed predisposition • Corneal cytology (lymphocytes, plasma cells, administered q 24-48h.
eosinophils, ± mast cells); after application • Transition to topical cyclosporine 0.2%
RISK FACTORS of a topical ophthalmic anesthetic, the blunt may be appropriate in some cases to replace
There is a tenuous association between feline end of a scalpel blade or cytobrush is gently topical steroids. Other cases may benefit from
herpesvirus infection (FHV) and eosinophilic scraped across the conjunctiva or cornea to the addition of cyclosporine to the steroid
keratitis, but evidence of active infection is gather cells. The slide is stained routinely. regimen to reduce the frequency of topical
lacking in most affected cats. steroid use.
Advanced or Confirmatory Testing
Clinical Presentation Corneal or conjunctival biopsy of affected Possible Complications
DISEASE FORMS/SUBTYPES tissue Recrudescence of latent herpesvirus may rarely
Eosinophilic keratitis can be localized to the occur with the use of corticosteroids and the
cornea or extend into the conjunctiva or can TREATMENT stress associated with veterinary visits and
be limited to the conjunctiva. The lesions most frequent treatments.
often appear plaquelike but can be thin and Treatment Overview
consist more of vascularization or be masslike. Eosinophilic keratitis responds similarly to Recommended Monitoring
other immune-mediated surface ocular dis- Monitoring q 1-2 weeks should be done during
HISTORY, CHIEF COMPLAINT eases, and immunomodulatory therapy is the the initial treatment and tapering phases. Then
Ocular discharge and a strange appearance to
the eye(s) are the most common complaints.
Cats rarely show signs of discomfort unless
a corneal ulcer develops concurrently. Ocular
discharge is seen in many cats. Vision can be
affected if the corneal opacities interfere with
the visual axis.
PHYSICAL EXAM FINDINGS
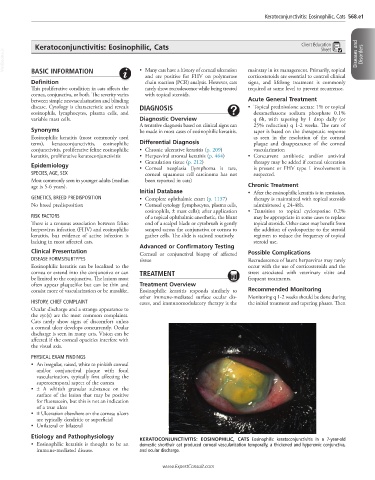
• An irregular, raised, white to pinkish corneal
and/or conjunctival plaque with focal
vascularization, typically first affecting the
superotemporal aspect of the cornea
• ± A whitish granular substance on the
surface of the lesion that may be positive
for fluorescein, but this is not an indication
of a true ulcer
• ± Ulceration elsewhere on the cornea; ulcers
are typically dendritic or superficial
• Unilateral or bilateral
Etiology and Pathophysiology KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS: EOSINOPHILIC, CATS Eosinophilic keratoconjunctivitis in a 7-year-old
• Eosinophilic keratitis is thought to be an domestic shorthair cat produced corneal vascularization temporally, a thickened and hyperemic conjunctiva,
immune-mediated disease. and ocular discharge.
www.ExpertConsult.com