Page 1623 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 1623
Pregnancy 817
outcross matings generally result in higher • Embryos migrate within the uterus and may pregnancy if the ultrasonographer is
pregnancy rates and larger litter sizes. Litter implant in the horn ipsilateral or contralateral inexperienced or the embryonic vesicle is
VetBooks.ir breeds have fewer offspring/litter. • Implantation occurs 15-17 days post LH ○ Fetal viability can be readily assessed by Diseases and Disorders
too small to visualize or obscured by viscera.
size also depends on maternal size; smaller
to ovulation.
surge in the bitch (14-15 days post LH surge
evaluating fetal heart rates after 25 days
RISK FACTORS
in the queen).
post LH surge.
Intact females exposed to intact males • Pregnancy is progesterone dependent ○ Gestational age can be estimated by
throughout gestation. Corpora luteal produc- fetal measurements and presence of fetal
GEOGRAPHY AND SEASONALITY tion of progesterone is required for pregnancy structures.
• Canine: most domestic breeds cycle twice maintenance. Prolactin is luteotropic and ○ Litter size can only be approximated.
yearly irrespective of season, with the maintains the corpus luteum during the Accurate counts are especially difficult
potential to become pregnant during each second half of pregnancy in dogs and cats. in late gestation or with large litters.
estrous cycle. Wolf hybrids cycle annually • Serum relaxin: relaxin is a hormone produced
during the spring (long-day breeders), and DIAGNOSIS by the placenta and is a confirmatory test
basenjis and Tibetan mastiffs cycle annually of pregnancy 30 days post LH surge. A
during autumn (short-day breeders). Diagnostic Overview commercially available test is labeled for
• Feline: cats are polyestrous, long-day breed- Transabdominal ultrasound (>20 days post dogs and has been validated for use in cats.
ers (queening during spring and summer) LH surge) is the most informative method ○ False-positives may result when relaxin
with seasonal anestrus during the winter to confirm pregnancy, but it also requires the levels remain elevated after fetal death (up
months. It is possible for a queen to have greatest experience. All methods of diagnosis to 2 days) or in cases of large ovarian cysts
multiple litters each year. Indoor housing may result in misdiagnosis if performed too (queens).
with extended hours of artificial lighting may early in gestation and warrant repeat evaluation ○ False-negatives can occur in early preg-
eliminate the anestrus period. 1-2 weeks later if a definitive diagnosis cannot nancy or in singleton litters that do not
be made. generate sufficiently elevated relaxin for
ASSOCIATED DISORDERS detection.
• Insulin resistance (pregnancy-associated Differential Diagnosis ○ Litter size and fetal viability do not cor-
diabetes) • Pyometra relate with relaxin concentrations.
• Pregnancy anemia • Mucometra • Abdominal radiographs: pregnancy can be
• Pyometra (p. 854) • Overt false pregnancy/pseudocyesis diagnosed by visualization of ossified fetal
• Hydrops (amnion, allantois, or fetal anasarca) • Ectopic pregnancy skeletons after 45 days post LH surge.
• Overt false pregnancy/pseudocyesis (p. 831) ○ False-negatives may occur with small litters
• Abortion (p. 2) or early embryonic loss Initial Database if a full colon obscures fetuses.
• Mammary hyperplasia (cats) • Transabdominal ultrasound: embryonic ○ False-negatives may occur before 45 days
vesicles can be detected as early as 20 days post LH surge.
Clinical Presentation post LH surge (16 days post LH surge in ○ Fetal loss of viability can be evaluated by
HISTORY, CHIEF COMPLAINT cats). The embryo can be detected after 25 fetal posture (appearance of disarticula-
• Intentional breeding days post LH surge. tion), bone juxtaposition (especially skull),
• Unintentional breeding ○ False-positives (diagnosis of pregnancy in and presence of intrafetal gas.
• Unexplained weight gain a nonpregnant animal) may result from ○ Estimation of whelping date based on
• Unexplained mammary development and misinterpretation of early pyometra or fetal structures (tooth buds and digits)
lactation mucometra or misidentifying fluid-filled is unreliable.
• Nesting behavior loops of bowel. ○ Litter size is most reliably estimated by
○ False-negatives (diagnosis of no pregnancy late-term radiographs during the last week
PHYSICAL EXAM FINDINGS in a pregnant animal) may occur in early of gestation.
• Embryonic vesicles or fetuses palpable
abdominally
○ Embryonic vesicles are palpable approxi-
mately 25-35 days after the LH surge.
○ Fetuses are palpable approximately 45 days
after the LH surge.
• Mammary development and lactation usually
emerge in the last 2 weeks of pregnancy.
Etiology and Pathophysiology
• Ovulation occurs 48 hours post LH surge
in dogs and 48 hours after breeding in
cats.
○ Bitches are most fertile 2-4 days after
ovulation (4-6 days post LH surge);
however, pregnancy can result from breed-
ings preceding ovulation by as much as 7
days if the sperm survive in the uterine
tubes until the ova mature.
• Fertilization occurs in the uterine tube
(ampulla-isthmus junction), and the embryos
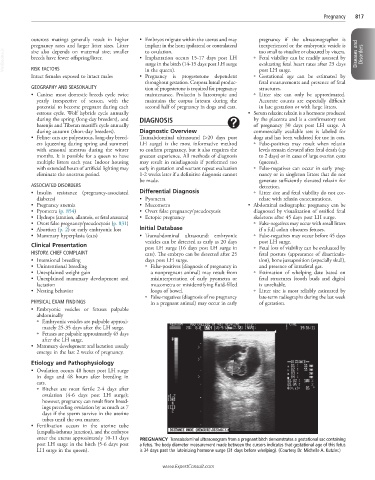
enter the uterus approximately 10-11 days PREGNANCY Transabdominal ultrasonogram from a pregnant bitch demonstrates a gestational sac containing
post LH surge in the bitch (5-6 days post a fetus. The body diameter measurement made between the cursors indicates that gestational age of this fetus
LH surge in the queen). is 34 days past the luteinizing hormone surge (31 days before whelping). (Courtesy Dr. Michelle A. Kutzler.)
www.ExpertConsult.com