Page 238 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 238
Atrioventricular Block 103
First-degree • Mobitz type II second-degree AV block, no
overt clinical signs: fair to good
VetBooks.ir A AV block and/or overt clinical signs present: Diseases and Disorders
• High-grade Mobitz type II second-degree
guarded to poor without treatment, but
pacemaker implantation
Second-degree generally good to excellent with permanent
• Third-degree AV block: poor without treat-
ment; generally good to excellent with
permanent pacemaker implantation (better
without CHF)
• After pacemaker placement (mainly in dogs
with third-degree AV block), clinical signs
B resolve in 92% of dogs and 1-, 3-, and 5-year
survival rates = 86%, 65%, and 39%,
respectively.
PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS
Comments
• First-degree AV block does not cause clinical
signs; it serves as clue that an underlying
C cardiac or systemic problem may (or may
not) be present (i.e., new first-degree AV
Third-degree block may be indicator of drug toxicosis if
a patient is receiving a drug that delays AV
nodal conduction (e.g., digoxin).
• Mobitz type I second-degree AV block
rarely causes clinical signs and does not
predict degeneration to Mobitz type II
second-degree AV block or third-degree
D AV block.
• For AV block requiring pacemaker implanta-
tion, ventricular antiarrhythmic agents are
contraindicated until artificial pacing is
established due to potential for suppression
of ventricular escape foci.
• Therapy for CHF can usually be tapered or
E discontinued after pacemaker implantation.
• Clinical signs may be subtle (e.g., progressive
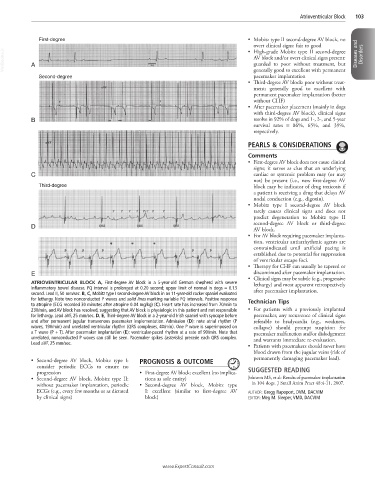
ATRIOVENTRICULAR BLOCK A, First-degree AV block in a 5-year-old German shepherd with severe lethargy) and most apparent retrospectively
inflammatory bowel disease. PQ interval is prolonged at 0.20 second; upper limit of normal in dogs = 0.13 after pacemaker implantation.
second. Lead II, 50 mm/sec. B, C, Mobitz type I second-degree AV block in an 11-year-old cocker spaniel evaluated
for lethargy. Note two nonconducted P waves and solid lines marking variable PQ intervals. Positive response Technician Tips
to atropine (ECG recorded 30 minutes after atropine 0.04 mg/kg) (C). Heart rate has increased from 70/min to
230/min, and AV block has resolved, suggesting that AV block is physiologic in this patient and not responsible • For patients with a previously implanted
for lethargy. Lead aVF, 25 mm/sec. D, E, Third-degree AV block in a 2-year-old Irish spaniel with syncope before pacemaker, any recurrence of clinical signs
and after permanent jugular transvenous pacemaker implementation. Admission (D): note atrial rhythm (P referable to bradycardia (e.g., weakness,
waves, 190/min) and unrelated ventricular rhythm (QRS complexes, 40/min). One P wave is superimposed on collapse) should prompt suspicion for
a T wave (P + T). After pacemaker implantation (E): ventricular-paced rhythm at a rate of 90/min. Note that pacemaker malfunction and/or dislodgement
unrelated, nonconducted P waves can still be seen. Pacemaker spikes (asterisks) precede each QRS complex. and warrants immediate re-evaluation.
Lead aVF, 25 mm/sec.
• Patients with pacemakers should never have
blood drawn from the jugular veins (risk of
• Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I: PROGNOSIS & OUTCOME permanently damaging pacemaker lead).
consider periodic ECGs to ensure no
progression • First-degree AV block: excellent (no implica- SUGGESTED READING
• Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II: tions as sole entity) Johnson MS, et al: Results of pacemaker implantation
without pacemaker implantation, periodic • Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type in 104 dogs. J Small Anim Pract 48:4-11, 2007.
ECGs (e.g., every few months or as dictated I: excellent (similar to first-degree AV AUTHOR: Gregg Rapoport, DVM, DACVIM
by clinical signs) block) EDITOR: Meg M. Sleeper, VMD, DACVIM
www.ExpertConsult.com