Page 2568 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2568
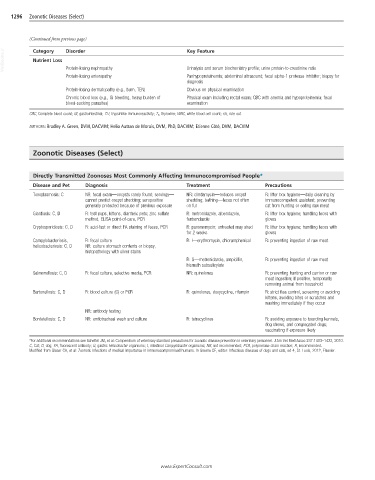
1296 Zoonotic Diseases (Select)
(Continued from previous page)
VetBooks.ir Category Disorder Key Feature
Nutrient Loss
Protein-losing nephropathy
Urinalysis and serum biochemistry profile; urine protein-to-creatinine ratio
Protein-losing enteropathy Panhypoproteinemia; abdominal ultrasound; fecal alpha-1 protease inhibitor; biopsy for
diagnosis
Protein-losing dermatopathy (e.g., burn, TEN) Obvious on physical examination
Chronic blood loss (e.g., GI bleeding, heavy burden of Physical exam including rectal exam; CBC with anemia and hypoproteinemia; fecal
blood-sucking parasites) examination
CBC, Complete blood count; GI, gastrointestinal; TLI, trypsinlike immunoreactivity; T 4, thyroxine; WBC, white blood cell count; r/o, rule out.
AUTHORS: Bradley A. Green, DVM, DACVIM; Helio Autran de Morais, DVM, PhD, DACVIM; Etienne Côté, DVM, DACVIM
Zoonotic Diseases (Select)
Directly Transmitted Zoonoses Most Commonly Affecting Immunocompromised People*
Disease and Pet Diagnosis Treatment Precautions
Toxoplasmosis: C NR: fecal exam—oocysts rarely found; serology— NR: clindamycin—reduces oocyst R: litter box hygiene—daily cleaning by
cannot predict oocyst shedding; seropositive shedding; bathing—feces not often immunocompetent assistant; preventing
generally protected because of previous exposure on fur cat from hunting or eating raw meat
Giardiasis: C, D R: test pups, kittens, diarrheic pets; zinc sulfate R: metronidazole, albendazole, R: litter box hygiene; handling feces with
method, ELISA point-of-care, PCR fenbendazole gloves
Cryptosporidiosis: C, D R: acid-fast or direct FA staining of feces, PCR R: paromomycin; untreated may shed R: litter box hygiene; handling feces with
for 2 weeks gloves
Campylobacteriosis, R: fecal culture R: I—erythromycin, chloramphenicol R: preventing ingestion of raw meat
helicobacteriosis: C, D NR: culture stomach contents or biopsy,
histopathology with silver stains
R: G—metronidazole, ampicillin, R: preventing ingestion of raw meat
bismuth subsalicylate
Salmonellosis: C, D R: fecal culture, selective media, PCR NR: quinolones R: preventing hunting and carrion or raw
meat ingestion; if positive, temporarily
removing animal from household
Bartonellosis: C, D R: blood culture (C) or PCR R: quinolones, doxycycline, rifampin R: strict flea control, screening or avoiding
kittens, avoiding bites or scratches and
washing immediately if they occur
NR: antibody testing
Bordetellosis: C, D NR: endotracheal wash and culture R: tetracyclines R: avoiding exposure to boarding kennels,
dog shows, and congregated dogs;
vaccinating if exposure likely
*For additional recommendations see Scheftel JM, et al: Compendium of veterinary standard precautions for zoonotic disease prevention in veterinary personnel. J Am Vet Med Assoc 237:1403–1422, 2010.
C, Cat; D, dog; FA, fluorescent antibody; G, gastric Helicobacter organisms; I, intestinal Campylobacter organisms; NR, not recommended; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; R, recommended.
Modified from Glaser CA, et al: Zoonotic infections of medical importance in immunocompromised humans. In Greene CE, editor: Infectious diseases of dogs and cats, ed 4, St. Louis, 2012, Elsevier.
www.ExpertConsult.com
www
.ExpertConsult.com