Page 508 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 508
228.e2 Cutaneous Cysts
Cutaneous Cysts
VetBooks.ir
HISTORY, CHIEF COMPLAINT
BASIC INFORMATION
• Evaluation of fluctuant to solid, nonpainful, • Solitary follicular cysts may develop sec-
ondary to dermal fibrosis, microtrauma, or
Definition mass in skin, on eyelid or ear blockage of follicular ostia.
Generic term for any epithelial-lined cavity • Often an incidental finding
containing fluid or solid material; common, DIAGNOSIS
benign, variably sized, cutaneous masses are PHYSICAL EXAM FINDINGS
found in the skin or around eyelids. Classifica- • Variably sized, 0.5 to > 5 cm, soft to fluctu- Diagnostic Overview
tion depends on identification of the lining of ant to firm dermal or subcutaneous masses, Diagnosis is based on finding single or multiple
epithelium or structure from which the cyst usually asymptomatic cutaneous masses with varying degrees of
arose. • Ruptured cysts can drain yellow to brown central fluctuation and/or draining exudate.
liquid, exude caseous material, and usually Cytologic evaluation of fine-needle aspiration
Synonym refill over time. They may become inflamed and/or histologic evaluation of excisional biopsy
Inclusion cyst and infected, causing local cellulitis pain and/ can confirm. Aspiration of feline ceruminous
or pruritus. cysts reveals black-blue debris with fine granular
Epidemiology • Multiple follicular cysts may be noted over texture.
SPECIES, AGE, SEX the dorsal midline or pressure points.
Dogs: common; cats: rare. Solitary cysts • Multiple follicular cysts can cause otitis and Differential Diagnosis
can occur at any age. Multiple cysts may be manifest as stenotic ear canals (rare). • Any type of benign or malignant subcutane-
congenital or breed related. • Dermoid cysts in cats are rare but may be ous neoplasm, foreign body, or infection
associated with paraparesis. • Keratoacanthoma (intracutaneous cornify-
GENETICS, BREED PREDISPOSITION • Feline ceruminous cystomatosis: multiple, ing epithelioma) usually has a pore with
• Dermoid cysts: boxers, Kerry blue terriers, bluish black papules, vesicles, and/or nodules, a keratinous plug. May be multiple and
Rhodesian ridgebacks (consider dermoid most commonly found in the ear canals or generalized
sinus more likely) eyelids • Papilloma
• Follicular cysts: boxers, shih tzus, schnauzers, • Trichofolliculoma
basset hounds Etiology and Pathophysiology • Cutaneous horn
• Ceruminous cystomatosis: Abyssinian, • Majority of cysts are follicular and classified • Caseous abscess
Himalayan, Persian, or domestic short hair as infundibular, matricial, or a hybrid type, • Interdigital abscess/furunculosis
based on location of development in the hair • Focal mucinosis especially in Shar-pei dogs
RISK FACTORS follicle, hair follicle matrix, or a combination
Age related, frictional apposition, common in of the two, respectively. Initial Database
areas with chronic inflammatory skin disease • Multiple follicular cysts likely congenital, as • Fine-needle aspirate with cytologic exami-
and/or pressure point or trauma are dermoid cysts nation to rule out tumor (e.g., mast cell);
Clinical Presentation
DISEASE FORMS/SUBTYPES
Follicular cysts, infundibular cysts, isthmus
catagen cyst, metrical cyst, hybrid cyst, dermoid
cyst, epitrichial (apocrine) sweat gland cyst,
sebaceous gland cyst, branchial cyst, ceruminous
gland cyst
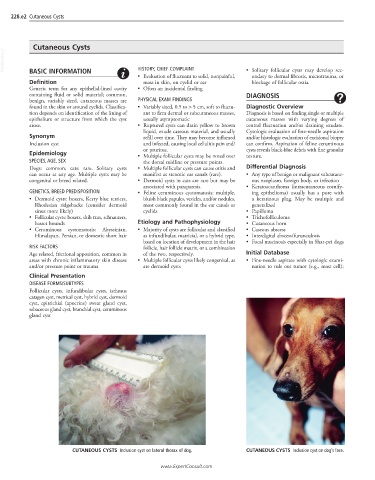
CUTANEOUS CYSTS Inclusion cyst on lateral thorax of dog. CUTANEOUS CYSTS Inclusion cyst on dog’s face.
www.ExpertConsult.com