Page 966 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 966
938 PART VIII Reproductive System Disorders
VetBooks.ir
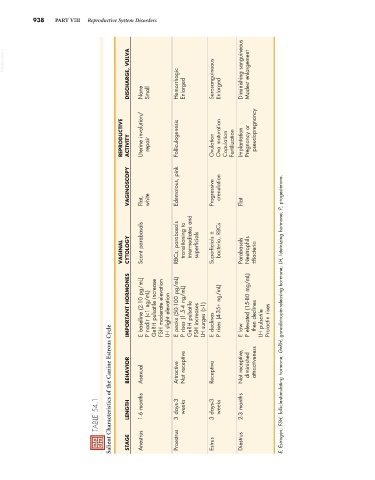
DISCHARGE, VULVA None Small Hemorrhagic Enlarged Serosanguineous Enlarged Diminishing sanguineous Modest enlargement
REPRODUCTIVE ACTIVITY Uterine involution/ repair Folliculogenesis Ovulation Ova maturation Copulation Fertilization Implantation Pregnancy or pseudopregnancy
VAGINOSCOPY Flat, white Edematous, pink Progressive crenulation Flat
VAGINAL CYTOLOGY Scant parabasals RBCs, parabasals transitioning to intermediates and superficials Superficials ± bacteria, RBCs Parabasals Neutrophils ±Bacteria
IMPORTANT HORMONES E baseline (2-10 pg/mL) P nadir (<1 ng/mL) GnRH pulsatile increase FSH moderate elevation LH slight elevation E peaks (50-100 pg/mL) P rises (1.5-4 ng/mL) GnRH pulsatile FSH increases LH surges (>1) E declines P rises (4-35+ ng/mL) E low P elevated (15-80 mg/mL) then declines LH pulsatile Prolactin rises E, Estrogen; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; LH, luteinizing h
Salient Characteristics of the Canine Estrous Cycle
BEHAVIOR Asexual Attractive Not receptive Receptive Not receptive, diminished attractiveness
TABLE 54.1 LENGTH 1-6 months 3 days-3 weeks 3 days-3 weeks 2-3 months
STAGE Anestrus Proestrus Estrus Diestrus