Page 1350 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1350
VetBooks.ir
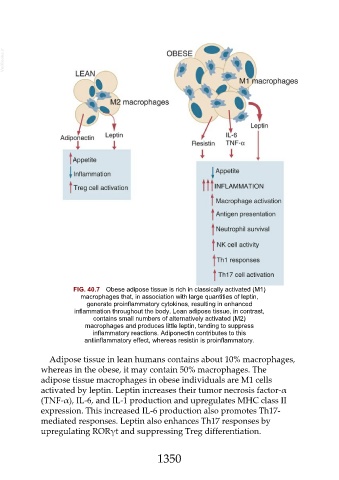
FIG. 40.7 Obese adipose tissue is rich in classically activated (M1)
macrophages that, in association with large quantities of leptin,
generate proinflammatory cytokines, resulting in enhanced
inflammation throughout the body. Lean adipose tissue, in contrast,
contains small numbers of alternatively activated (M2)
macrophages and produces little leptin, tending to suppress
inflammatory reactions. Adiponectin contributes to this
antiinflammatory effect, whereas resistin is proinflammatory.
Adipose tissue in lean humans contains about 10% macrophages,
whereas in the obese, it may contain 50% macrophages. The
adipose tissue macrophages in obese individuals are M1 cells
activated by leptin. Leptin increases their tumor necrosis factor-α
(TNF-α), IL-6, and IL-1 production and upregulates MHC class II
expression. This increased IL-6 production also promotes Th17-
mediated responses. Leptin also enhances Th17 responses by
upregulating RORγt and suppressing Treg differentiation.
1350