Page 1353 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1353
VetBooks.ir
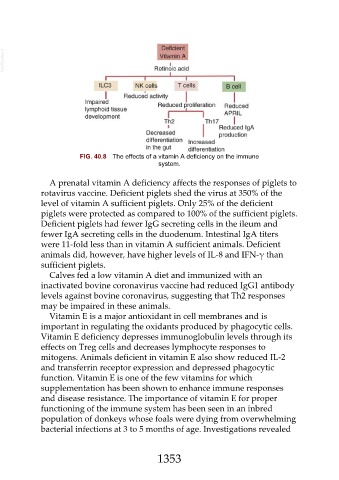
FIG. 40.8 The effects of a vitamin A deficiency on the immune
system.
A prenatal vitamin A deficiency affects the responses of piglets to
rotavirus vaccine. Deficient piglets shed the virus at 350% of the
level of vitamin A sufficient piglets. Only 25% of the deficient
piglets were protected as compared to 100% of the sufficient piglets.
Deficient piglets had fewer IgG secreting cells in the ileum and
fewer IgA secreting cells in the duodenum. Intestinal IgA titers
were 11-fold less than in vitamin A sufficient animals. Deficient
animals did, however, have higher levels of IL-8 and IFN-γ than
sufficient piglets.
Calves fed a low vitamin A diet and immunized with an
inactivated bovine coronavirus vaccine had reduced IgG1 antibody
levels against bovine coronavirus, suggesting that Th2 responses
may be impaired in these animals.
Vitamin E is a major antioxidant in cell membranes and is
important in regulating the oxidants produced by phagocytic cells.
Vitamin E deficiency depresses immunoglobulin levels through its
effects on Treg cells and decreases lymphocyte responses to
mitogens. Animals deficient in vitamin E also show reduced IL-2
and transferrin receptor expression and depressed phagocytic
function. Vitamin E is one of the few vitamins for which
supplementation has been shown to enhance immune responses
and disease resistance. The importance of vitamin E for proper
functioning of the immune system has been seen in an inbred
population of donkeys whose foals were dying from overwhelming
bacterial infections at 3 to 5 months of age. Investigations revealed
1353