Page 346 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 346
Serology and immunology 315
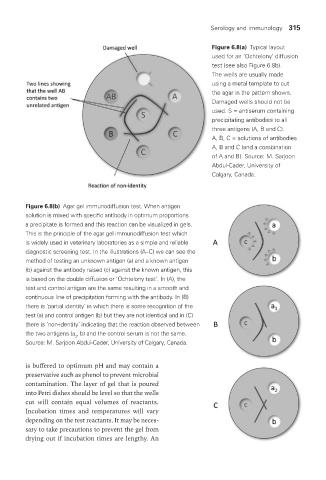
Figure 6.8(a) Typical layout
used for an ‘Ochtelony’ diffusion
test (see also Figure 6.8b).
The wells are usually made
using a metal template to cut
the agar in the pattern shown.
Damaged wells should not be
used. S = antiserum containing
precipitating antibodies to all
three antigens (A, B and C).
A, B, C = solutions of antibodies
A, B and C (and a combination
of A and B). Source: M. Sarjoon
Abdul-Cader, University of
Calgary, Canada.
Figure 6.8(b) Agar gel immunodiffusion test. When antigen
solution is mixed with specific antibody in optimum proportions
a precipitate is formed and this reaction can be visualized in gels.
This is the principle of the agar gel immunodiffusion test which
is widely used in veterinary laboratories as a simple and reliable
diagnostic screening test. In the illustrations (A–C) we can see the
method of testing an unknown antigen (a) and a known antigen
(b) against the antibody raised (c) against the known antigen, this
is based on the double diffusion or ‘Ochtelony test’. In (A), the
test and control antigen are the same resulting in a smooth and
continuous line of precipitation forming with the antibody. In (B)
there is ‘partial identity’ in which there is some recognition of the
test (a) and control antigen (b) but they are not identical and in (C)
there is ‘non-identity’ indicating that the reaction observed between
the two antigens (a , b) and the control serum is not the same.
2
Source: M. Sarjoon Abdul-Cader, University of Calgary, Canada.
is buffered to optimum pH and may contain a
preservative such as phenol to prevent microbial
contamination. The layer of gel that is poured
into Petri dishes should be level so that the wells
cut will contain equal volumes of reactants.
Incubation times and temperatures will vary
depending on the test reactants. It may be neces-
sary to take precautions to prevent the gel from
drying out if incubation times are lengthy. An
Vet Lab.indb 315 26/03/2019 10:26