Page 351 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 351
320 Susan C. Cork, M. Faizal Abdul Careem and M. Sarjoon Abdul-Cader
endpoint of the reaction. It may be necessary to Direct method
titrate the antigen prior to the test to determine
that the optimum concentration of antibody is In this test, the fluorescent dye is conjugated
used. with a specific antibody to the antigen that is
to be demonstrated. For example, if it is rabies
virus (negri bodies in brain tissue) under test,
then the brain smears are incubated with anti-
Fluorescent antibody tests
rabies (IgG) coupled with fluorescein.
Fluorescent dyes such as fluorescein isothiocya-
nate (FITC) and rhodamine can be conjugated Indirect method
(coupled) with antibodies without interfer-
ing with the ability of the antibody to combine In this test, an unconjugated antibody is applied
with a specific antigen. This antigen–antibody- directly to the test sample. An antigen–antibody
fluorescent dye combination can then be viewed reaction (coupling) at this stage may take place
using a fluorescent microscope (Figure 6.11). but cannot be viewed under a fluorescent micro-
This principle is employed in veterinary labora- scope since no fluorescent label is present. The
tories to detect microorganisms. tissue is then washed to remove the unattached
Two ways of carrying out this test are detailed antibody. A fluorescent conjugated anti-immu-
below. noglobulin to the unconjugated antibody is now
applied. If antibodies are still present (which
will only be the case if they are bound to specific
antigen in the test material) conjugation of the
immunoglobulin/anti-immunoglobulin/fluores-
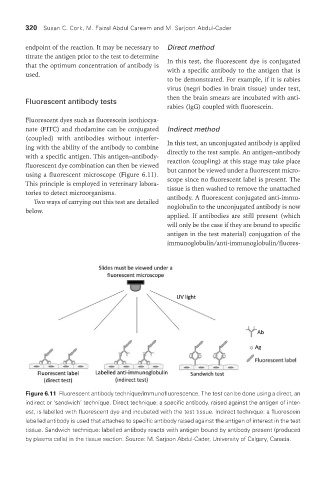
Figure 6.11 Fluorescent antibody technique/immunofluorescence. The test can be done using a direct, an
indirect or ‘sandwich’ technique. Direct technique: a specific antibody, raised against the antigen of inter-
est, is labelled with fluorescent dye and incubated with the test tissue. Indirect technique: a fluorescein
labelled antibody is used that attaches to specific antibody raised against the antigen of interest in the test
tissue. Sandwich technique: labelled antibody reacts with antigen bound by antibody present (produced
by plasma cells) in the tissue section. Source: M. Sarjoon Abdul-Cader, University of Calgary, Canada.
Vet Lab.indb 320 26/03/2019 10:26