Page 384 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 384
Clinical chemistry 353
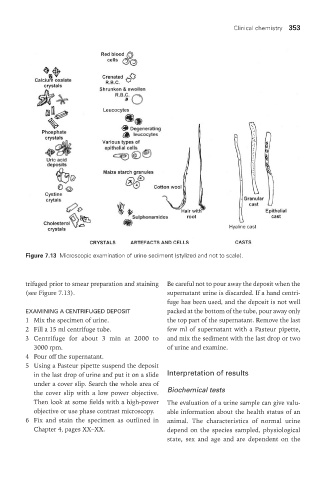
Figure 7.13 Microscopic examination of urine sediment (stylized and not to scale).
trifuged prior to smear preparation and staining Be careful not to pour away the deposit when the
(see Figure 7.13). supernatant urine is discarded. If a hand centri-
fuge has been used, and the deposit is not well
ExaMInInG a cEntrIFuGEd dEPoSIt packed at the bottom of the tube, pour away only
1 Mix the specimen of urine. the top part of the supernatant. Remove the last
2 Fill a 15 ml centrifuge tube. few ml of supernatant with a Pasteur pipette,
3 Centrifuge for about 3 min at 2000 to and mix the sediment with the last drop or two
3000 rpm. of urine and examine.
4 Pour off the supernatant.
5 Using a Pasteur pipette suspend the deposit
in the last drop of urine and put it on a slide Interpretation of results
under a cover slip. Search the whole area of
the cover slip with a low power objective. Biochemical tests
Then look at some fields with a high-power The evaluation of a urine sample can give valu-
objective or use phase contrast microscopy. able information about the health status of an
6 Fix and stain the specimen as outlined in animal. The characteristics of normal urine
Chapter 4, pages XX–XX. depend on the species sampled, physiological
state, sex and age and are dependent on the
Vet Lab.indb 353 26/03/2019 10:26