Page 388 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 388
Clinical chemistry 357
because of their curiosity and because they tend (a)
to be less discriminating in what they taste and
eat than other species such as goats, horses and
swine, are the most likely to be poisoned from
exposure to lead. This often occurs because of
discarded batteries being left in fields. Another
source of lead can develop around industrial
sites and pump jacks where oil leaks out as it
is being extracted from underground sources.
Horses are most likely to be exposed by chewing
at fences that have been painted with lead-con-
taining paint, similar to cases of lead poisoning
in puppies when they chew toys that have been
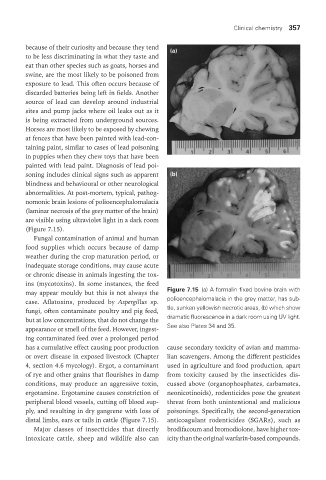
painted with lead paint. Diagnosis of lead poi-
soning includes clinical signs such as apparent (b)
blindness and behavioural or other neurological
abnormalities. At post-mortem, typical, pathog-
nomonic brain lesions of polioencephalomalacia
(laminar necrosis of the grey matter of the brain)
are visible using ultraviolet light in a dark room
(Figure 7.15).
Fungal contamination of animal and human
food supplies which occurs because of damp
weather during the crop maturation period, or
inadequate storage conditions, may cause acute
or chronic disease in animals ingesting the tox-
ins (mycotoxins). In some instances, the feed
may appear mouldy but this is not always the Figure 7.15 (a) A formalin fixed bovine brain with
case. Aflatoxins, produced by Aspergillus sp. polioencephalomalacia in the grey matter, has sub-
fungi, often contaminate poultry and pig feed, tle, sunken yellowish necrotic areas, (b) which show
but at low concentrations, that do not change the dramatic fluorescence in a dark room using UV light.
appearance or smell of the feed. However, ingest- See also Plates 34 and 35.
ing contaminated feed over a prolonged period
has a cumulative effect causing poor production cause secondary toxicity of avian and mamma-
or overt disease in exposed livestock (Chapter lian scavengers. Among the different pesticides
4, section 4.6 mycology). Ergot, a contaminant used in agriculture and food production, apart
of rye and other grains that flourishes in damp from toxicity caused by the insecticides dis-
conditions, may produce an aggressive toxin, cussed above (organophosphates, carbamates,
ergotamine. Ergotamine causes constriction of neonicotinoids), rodenticides pose the greatest
peripheral blood vessels, cutting off blood sup- threat from both unintentional and malicious
ply, and resulting in dry gangrene with loss of poisonings. Specifically, the second-generation
distal limbs, ears or tails in cattle (Figure 7.15). anticoagulant rodenticides (SGARs), such as
Major classes of insecticides that directly brodifacoum and bromodiolone, have higher tox-
intoxicate cattle, sheep and wildlife also can icity than the original warfarin-based compounds.
Vet Lab.indb 357 26/03/2019 10:26