Page 391 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 391
360 Susan C. Cork, Willy Schauwers and Roy Halliwell
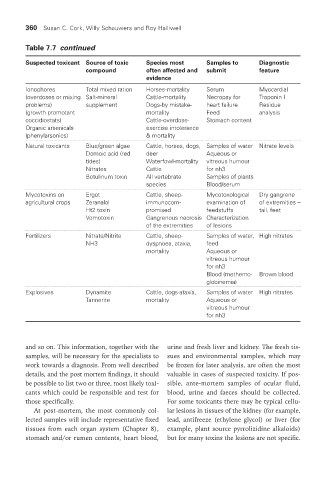
Table 7.7 continued
Suspected toxicant Source of toxic Species most Samples to diagnostic
compound often affected and submit feature
evidence
Ionophores Total mixed ration Horses-mortality Serum Myocardial
(overdoses or mixing Salt-mineral Cattle-mortality Necropsy for Troponin I
problems) supplement Dogs-by mistake- heart failure Residue
(growth promotant mortality Feed analysis
coccidiostats) Cattle-overdose- Stomach content
Organic arsenicals exercise intolerance
(phenylarsonics) & mortality
Natural toxicants Blue/green algae Cattle, horses, dogs, Samples of water Nitrate levels
Domoic acid (red deer Aqueous or
tides) Waterfowl-mortality vitreous humour
Nitrates Cattle for nh3
Botulinum toxin All vertebrate Samples of plants
species Blood/serum
Mycotoxins on Ergot Cattle, sheep- Mycotoxological Dry gangrene
agricultural crops Zeranalol immunocom- examination of of extremities –
Ht2 toxin promised feedstuffs tail, feet
Vomotoxin Gangrenous necrosis Characterization
of the extremities of lesions
Fertilizers Nitrate/Nitrite Cattle, sheep- Samples of water, High nitrates
NH3 dyspnoea, ataxia, feed
mortality Aqueous or
vitreous humour
for nh3
Blood (methemo- Brown blood
globinemia)
Explosives Dynamite Cattle, dogs-ataxia, Samples of water High nitrates
Tannerite mortality Aqueous or
vitreous humour
for nh3
and so on. This information, together with the urine and fresh liver and kidney. The fresh tis-
samples, will be necessary for the specialists to sues and environmental samples, which may
work towards a diagnosis. From well described be frozen for later analysis, are often the most
details, and the post mortem findings, it should valuable in cases of suspected toxicity. If pos-
be possible to list two or three, most likely toxi- sible, ante-mortem samples of ocular fluid,
cants which could be responsible and test for blood, urine and faeces should be collected.
those specifically. For some toxicants there may be typical cellu-
At post-mortem, the most commonly col- lar lesions in tissues of the kidney (for example,
lected samples will include representative fixed lead, antifreeze (ethylene glycol) or liver (for
tissues from each organ system (Chapter 8), example, plant source pyrrolizidine alkaloids)
stomach and/or rumen contents, heart blood, but for many toxins the lesions are not specific.
Vet Lab.indb 360 26/03/2019 10:26