Page 959 - Problem-Based Feline Medicine
P. 959
44 – THE CAT WITH GENERALIZED WEAKNESS 951
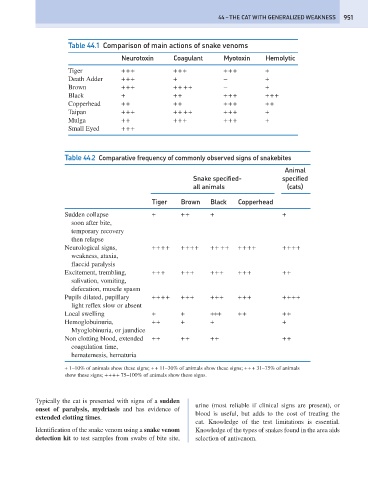
Table 44.1 Comparison of main actions of snake venoms
Neurotoxin Coagulant Myotoxin Hemolytic
Tiger +++ +++ +++ +
Death Adder +++ + − +
Brown +++ ++ ++ − +
Black + ++ +++ +++
Copperhead ++ ++ +++ ++
Taipan +++ ++ ++ +++ +
Mulga ++ +++ +++ +
Small Eyed +++
Table 44.2 Comparative frequency of commonly observed signs of snakebites
Animal
Snake specified- specified
all animals (cats)
Tiger Brown Black Copperhead
Sudden collapse + + + + +
soon after bite,
temporary recovery
then relapse
Neurological signs, ++++ ++++ ++ ++ ++++ ++++
weakness, ataxia,
flaccid paralysis
Excitement, trembling, +++ +++ +++ +++ ++
salivation, vomiting,
defecation, muscle spasm
Pupils dilated, pupillary ++++ +++ +++ +++ ++++
light reflex slow or absent
Local swelling + + +++ ++ ++
Hemoglobuinuria, ++ + + +
Myoglobinuria, or jaundice
Non clotting blood, extended ++ ++ ++ ++
coagulation time,
hematemesis, hematuria
+ 1–10% of animals show these signs; ++ 11–30% of animals show these signs; +++ 31–75% of animals
show these signs; ++++ 75–100% of animals show these signs.
Typically the cat is presented with signs of a sudden
urine (most reliable if clinical signs are present), or
onset of paralysis, mydriasis and has evidence of
blood is useful, but adds to the cost of treating the
extended clotting times.
cat. Knowledge of the test limitations is essential.
Identification of the snake venom using a snake venom Knowledge of the types of snakes found in the area aids
detection kit to test samples from swabs of bite site, selection of antivenom.