Page 960 - Problem-Based Feline Medicine
P. 960
952 PART 11 CAT WITH AN ABNORMAL GAIT
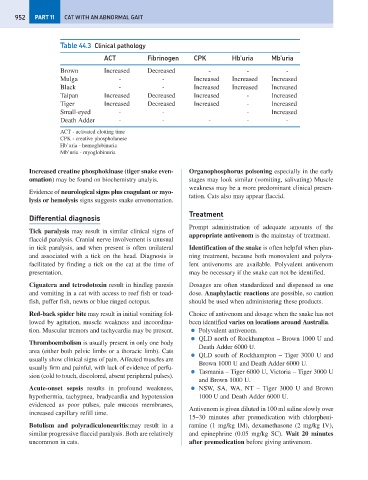
Table 44.3 Clinical pathology
ACT Fibrinogen CPK Hb’uria Mb’uria
Brown Increased Decreased - - -
Mulga - - Increased Increased Increased
Black - - Increased Increased Increased
Taipan Increased Decreased Increased - Increased
Tiger Increased Decreased Increased - Increased
Small-eyed - - - Increased
Death Adder - - - - -
ACT - activated clotting time
CPK - creative phospholanese
Hb’uria - hemoglobinuria
Mb’uria - myoglobinuria
Increased creatine phosphokinase (tiger snake even- Organophosphorus poisoning especially in the early
omation) may be found on biochemistry analyis. stages may look similar (vomiting, salivating) Muscle
weakness may be a more predominant clinical presen-
Evidence of neurological signs plus coagulant or myo-
tation. Cats also may appear flaccid.
lysis or hemolysis signs suggests snake envenomation.
Treatment
Differential diagnosis
Prompt administration of adequate amounts of the
Tick paralysis may result in similar clinical signs of
appropriate antivenom is the mainstay of treatment.
flaccid paralysis. Cranial nerve involvement is unusual
in tick paralysis, and when present is often unilateral Identification of the snake is often helpful when plan-
and associated with a tick on the head. Diagnosis is ning treatment, because both monovalent and polyva-
facilitated by finding a tick on the cat at the time of lent antivenoms are available. Polyvalent antivenom
presentation. may be necessary if the snake can not be identified.
Ciguatera and tetrodotoxin result in hindleg paresis Dosages are often standardized and dispensed as one
and vomiting in a cat with access to reef fish or toad- dose. Anaphylactic reactions are possible, so caution
fish, puffer fish, newts or blue ringed octopus. should be used when administering these products.
Red-back spider bite may result in initial vomiting fol- Choice of antivenom and dosage when the snake has not
lowed by agitation, muscle weakness and incoordina- been identified varies on locations around Australia.
tion. Muscular tremors and tachycardia may be present. ● Polyvalent antivenom.
● QLD north of Rockhampton – Brown 1000 U and
Thromboembolism is usually present in only one body
Death Adder 6000 U.
area (either both pelvic limbs or a thoracic limb). Cats
● QLD south of Rockhampton – Tiger 3000 U and
usually show clinical signs of pain. Affected muscles are
Brown 1000 U and Death Adder 6000 U.
usually firm and painful, with lack of evidence of perfu-
● Tasmania – Tiger 6000 U, Victoria – Tiger 3000 U
sion (cold to touch, discolored, absent peripheral pulses).
and Brown 1000 U.
Acute-onset sepsis results in profound weakness, ● NSW, SA, WA, NT – Tiger 3000 U and Brown
hypothermia, tachypnea, bradycardia and hypotension 1000 U and Death Adder 6000 U.
evidenced as poor pulses, pale mucous membranes,
Antivenom is given diluted in 100 ml saline slowly over
increased capillary refill time.
15–30 minutes after premedication with chlorpheni-
Botulism and polyradiculoneuritis:may result in a ramine (1 mg/kg IM), dexamethasone (2 mg/kg IV),
similar progressive flaccid paralysis. Both are relatively and epinephrine (0.05 mg/kg SC). Wait 20 minutes
uncommon in cats. after premedication before giving antivenom.