Page 52 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 52
18 Chapter 1
groove between DDFT and suspensory ligament, sup
plying the digital flexor tendons and the skin superficial
VetBooks.ir Median n.v.a. palmar nerve detaches a communicating branch that
to them. At the middle of the metacarpus, the medial
angles distolaterad in the subcutaneous fascia superfi
Proximal radial a. cial to the flexor tendons to join the lateral palmar
nerve. Branches from the dorsal branch of the ulnar
nerve ramify in the fascia and skin of the lateral aspect
Ulnar n. and of the metacarpus. Branches from the medial cutaneous
collateral ulnar a.v.
antebrachial nerve (itself a branch of the musculocuta
neous nerve) supply the medial and dorsal skin of the
Radial a.
metacarpus with the large dorsal branch reaching the
Palmar branch of median a. skin over the dorsomedial aspect of the fetlock.
Dorsal branch of ulnar n.
Palmar branch of ulnar n. Palmar Aspect
Lateral palmar n. The SDFT is deep to the skin and subcutaneous fas
cia throughout the length of the metacarpus. Dorsally,
Medial palmar a. it is intimately related to the DDFT. The latter, in turn,
lies against the palmar surface of the suspensory liga
Medial palmar n. ment (a.k.a. m. interosseus medius; middle or third
interosseous muscle). The carpal synovial sheath,
enclosing both digital flexor tendons, extends distad as
far as the middle of the metacarpus. At this level, the
DDFT is joined by its accessory ligament (carpal check
ligament or “inferior” check ligament), a distal con
tinuation of the palmar carpal ligament (Figure 1.32).
The medial and lateral lumbricales muscles, fleshy in
Deep branch of
lateral palmar n. other species, are reduced in the horse to fibrous slips
that originate from either side of the DDFT and insert
Proximal deep palmar arch in the fibrous tissue deep to the ergot. The lumbricales
in the pelvic limb tend to be better developed. The digi
tal synovial sheath around the digital flexor tendons is
Suspensory ligament present through the distal fourth of the metacarpus
(interosseus medius m.) (Figure 1.11).
Communicating branch (cut) The metacarpal groove, formed by the palmar surface
of the third metacarpal bone and the axial surfaces of
Medial palmar n. the second and fourth metacarpal bones, is occupied by
the suspensory ligament. The suspensory ligament arises
Lateral palmar n. from the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal
end of the third metacarpal bone (Figures 1.18 and
1.19). It is broad, relatively flat, and shorter than the
suspensory ligament of the hindlimb. Variable amounts
Medial palmar a.
of muscle fibers are seen within the mainly collagenous
suspensory ligament primarily in foals, in which these
are gradually replaced by collagen with musculoskeletal
maturation. In the distal fourth of the metacarpus, the
45
Superficial palmar arch suspensory ligament bifurcates to become associated
Lateral digital a. with the two proximal sesamoid bones. Each branch
makes a broad attachment across the abaxial surface of
Medial digital a. proximal sesamoid bone and blends with the origin of
the ipsilateral CSL (Figure 1.12). Two (medial and lat
eral) vestigial interosseous muscles originate on the
heads of the respective splint bones; their slender ten
dons pass distad alongside the splint bones and end near
the buttons by blending into the fascia of the fetlock.
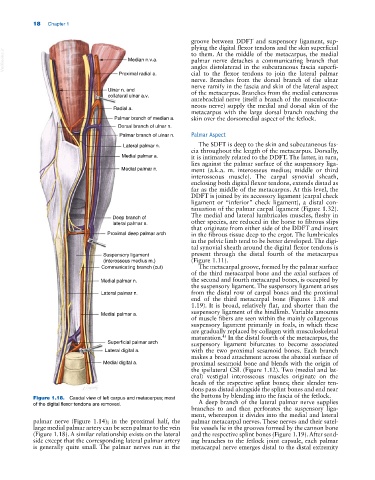
Figure 1.18. Caudal view of left carpus and metacarpus; most A deep branch of the lateral palmar nerve supplies
of the digital flexor tendons are removed.
branches to and then perforates the suspensory liga
ment, whereupon it divides into the medial and lateral
palmar nerve (Figure 1.14); in the proximal half, the palmar metacarpal nerves. These nerves and their satel
large medial palmar artery can be seen palmar to the vein lite vessels lie in the grooves formed by the cannon bone
(Figure 1.18). A similar relationship exists on the lateral and the respective splint bones (Figure 1.19). After send
side except that the corresponding lateral palmar artery ing branches to the fetlock joint capsule, each palmar
is generally quite small. The palmar nerves run in the metacarpal nerve emerges distal to the distal extremity