Page 277 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 277
262 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
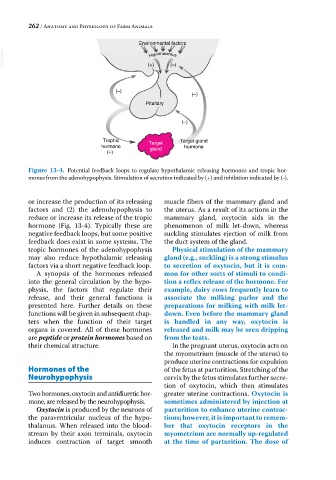
Environmental factors
VetBooks.ir (+) (–)
Hypothalamus
(–)
(–)
Pituitary
(–)
Trophic Target Target gland
hormone gland hormone
(+)
Figure 13-4. Potential feedback loops to regulate hypothalamic releasing hormones and tropic hor
mones from the adenohypophysis. Stimulation of secretion indicated by (+) and inhibition indicated by (‐).
or increase the production of its releasing muscle fibers of the mammary gland and
factors and (2) the adenohypophysis to the uterus. As a result of its actions in the
reduce or increase its release of the tropic mammary gland, oxytocin aids in the
hormone (Fig. 13‐4). Typically these are phenomenon of milk let‐down, whereas
negative feedback loops, but some positive suckling stimulates ejection of milk from
feedback does exist in some systems. The the duct system of the gland.
tropic hormones of the adenohypophysis Physical stimulation of the mammary
may also reduce hypothalamic releasing gland (e.g., suckling) is a strong stimulus
factors via a short negative feedback loop. to secretion of oxytocin, but it is com-
A synopsis of the hormones released mon for other sorts of stimuli to condi-
into the general circulation by the hypo tion a reflex release of the hormone. For
physis, the factors that regulate their example, dairy cows frequently learn to
release, and their general functions is associate the milking parlor and the
presented here. Further details on these preparations for milking with milk let‐
functions will be given in subsequent chap down. Even before the mammary gland
ters when the function of their target is handled in any way, oxytocin is
organs is covered. All of these hormones released and milk may be seen dripping
are peptide or protein hormones based on from the teats.
their chemical structure. In the pregnant uterus, oxytocin acts on
the myometrium (muscle of the uterus) to
produce uterine contractions for expulsion
Hormones of the of the fetus at parturition. Stretching of the
Neurohypophysis cervix by the fetus stimulates further secre
tion of oxytocin, which then stimulates
Two hormones, oxytocin and antidiuretic hor greater uterine contractions. Oxytocin is
mone, are released by the neurohypophysis. sometimes administered by injection at
Oxytocin is produced by the neurons of parturition to enhance uterine contrac-
the paraventricular nucleus of the hypo tions; however, it is important to remem-
thalamus. When released into the blood ber that oxytocin receptors in the
stream by their axon terminals, oxytocin myometrium are normally up‐regulated
induces contraction of target smooth at the time of parturition. The dose of