Page 423 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 423
408 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
Figure 21‐9 summarizes the absorptive fluid, where they are absorbed into lym-
phatics (Fig. 21‐10). The smallest of the
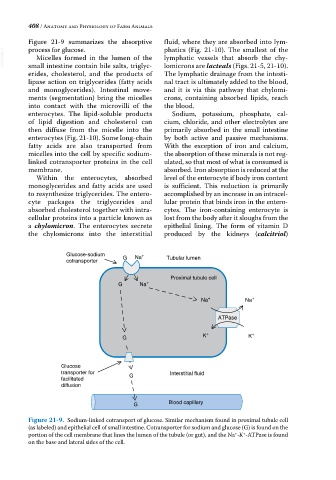
process for glucose.
VetBooks.ir small intestine contain bile salts, triglyc- lymphatic vessels that absorb the chy-
Micelles formed in the lumen of the
lomicrons are lacteals (Figs. 21-5, 21‐10).
erides, cholesterol, and the products of The lymphatic drainage from the intesti-
lipase action on triglycerides (fatty acids nal tract is ultimately added to the blood,
and monoglycerides). Intestinal move- and it is via this pathway that chylomi-
ments (segmentation) bring the micelles crons, containing absorbed lipids, reach
into contact with the microvilli of the the blood.
enterocytes. The lipid‐soluble products Sodium, potassium, phosphate, cal-
of lipid digestion and cholesterol can cium, chloride, and other electrolytes are
then diffuse from the micelle into the primarily absorbed in the small intestine
enterocytes (Fig. 21‐10). Some long‐chain by both active and passive mechanisms.
fatty acids are also transported from With the exception of iron and calcium,
micelles into the cell by specific sodium‐ the absorption of these minerals is not reg-
linked cotransporter proteins in the cell ulated, so that most of what is consumed is
membrane. absorbed. Iron absorption is reduced at the
Within the enterocytes, absorbed level of the enterocyte if body iron content
monoglycerides and fatty acids are used is sufficient. This reduction is primarily
to resynthesize triglycerides. The entero- accomplished by an increase in an intracel-
cyte packages the triglycerides and lular protein that binds iron in the entero-
absorbed cholesterol together with intra- cytes. The iron‐containing enterocyte is
cellular proteins into a particle known as lost from the body after it sloughs from the
a chylomicron. The enterocytes secrete epithelial lining. The form of vitamin D
the chylomicrons into the interstitial produced by the kidneys (calcitriol)
Glucose-sodium Na +
cotransporter G Tubular lumen
Proximal tubule cell
G Na +
Na + Na +
ATPase
G K + K +
Glucose
transporter for Interstitial fluid
facilitated G
diffusion
G Blood capillary
Figure 21-9. Sodium‐linked cotransport of glucose. Similar mechanism found in proximal tubule cell
(as labeled) and epithelial cell of small intestine. Cotransporter for sodium and glucose (G) is found on the
portion of the cell membrane that lines the lumen of the tubule (or gut), and the Na ‐K ‐ATPase is found
+
+
on the base and lateral sides of the cell.