Page 189 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 189
16 Imaging in Cardiovascular Disease 157
VetBooks.ir (a)
(b) (c)
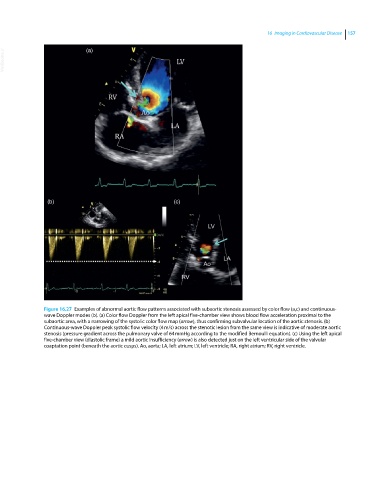
Figure 16.27 Examples of abnormal aortic flow patterns associated with subaortic stenosis assessed by color flow (a,c) and continuous‐
wave Doppler modes (b). (a) Color flow Doppler from the left apical five‐chamber view shows blood flow acceleration proximal to the
subaortic area, with a narrowing of the systolic color flow map (arrow), thus confirming subvalvular location of the aortic stenosis. (b)
Continuous‐wave Doppler peak systolic flow velocity (4 m/s) across the stenotic lesion from the same view is indicative of moderate aortic
stenosis (pressure gradient across the pulmonary valve of 64 mmHg according to the modified Bernoulli equation). (c) Using the left apical
five‐chamber view (diastolic frame) a mild aortic insufficiency (arrow) is also detected just on the left ventricular side of the valvular
coaptation point (beneath the aortic cusps). Ao, aorta; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.