Page 185 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 185
16 Imaging in Cardiovascular Disease 153
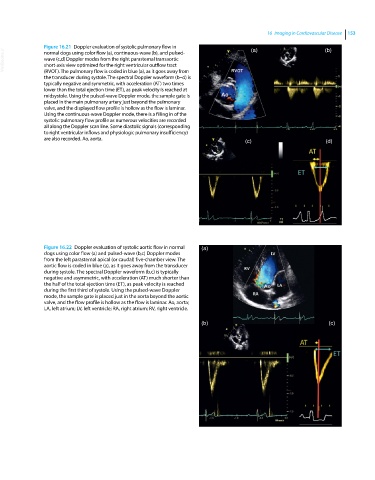
Figure 16.21 Doppler evaluation of systolic pulmonary flow in (a) (b)
VetBooks.ir wave (c,d) Doppler modes from the right parasternal transaortic
normal dogs using color flow (a), continuous‐wave (b), and pulsed‐
short‐axis view optimized for the right ventricular outflow tract
(RVOT). The pulmonary flow is coded in blue (a), as it goes away from
the transducer during systole. The spectral Doppler waveform (b–d) is
typically negative and symmetric, with acceleration (AT) two times
lower than the total ejection time (ET), as peak velocity is reached at
midsystole. Using the pulsed‐wave Doppler mode, the sample gate is
placed in the main pulmonary artery just beyond the pulmonary
valve, and the displayed flow profile is hollow as the flow is laminar.
Using the continuous‐wave Doppler mode, there is a filling in of the
systolic pulmonary flow profile as numerous velocities are recorded
all along the Doppler scan line. Some diastolic signals (corresponding
to right ventricular inflows and physiologic pulmonary insufficiency)
are also recorded. Ao, aorta. (c) (d)
Figure 16.22 Doppler evaluation of systolic aortic flow in normal (a)
dogs using color flow (a) and pulsed‐wave (b,c) Doppler modes
from the left parasternal apical (or caudal) five‐chamber view. The
aortic flow is coded in blue (a), as it goes away from the transducer
during systole. The spectral Doppler waveform (b,c) is typically
negative and asymmetric, with acceleration (AT) much shorter than
the half of the total ejection time (ET), as peak velocity is reached
during the first third of systole. Using the pulsed‐wave Doppler
mode, the sample gate is placed just in the aorta beyond the aortic
valve, and the flow profile is hollow as the flow is laminar. Ao, aorta;
LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.
(b) (c)