Page 18 - Avian Virology: Current Research and Future Trends
P. 18
Avian Influenza Virus | 11
and glycoproteins on the cell surface (Fig. 1.2) (Lamb, 1989). IAVs and Kim, 1993; Carr et al., 1997; Gruenke et al., 2002). Acidifi-
utilize clathrin-mediated and clathrin- and caveolin-independent cation of the endosome activates also the M2’s proton channel
endocytic pathways for entry (Rust et al., 2004). Upon acidifica- (Pinto et al., 1992). During the late endosomal phase, the influx
+
tion of the late endosome, the HA undergoes conformational of protons and potassium (K ) into the virus particle triggers the
changes that exposes the N-terminal fusion peptide on the HA2 dissociation of M1 from the vRNPs (Stauffer et al., 2014). The
subunit through a spring-loaded mechanism that results in the concerted action of HA and M2 in the endosome leads also to
fusion of the endosomal and viral membranes (Fig. 1.3) (Carr the widening of the fusion pore allowing the vRNPs to migrate
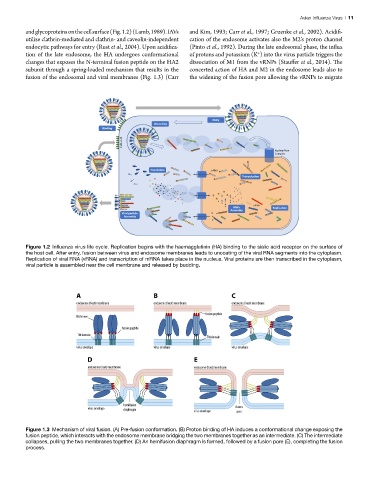
Figure 1.2 Influenza virus life cycle. Replication begins with the haemagglutinin (HA) binding to the sialic acid receptor on the surface of
the host cell. After entry, fusion between virus and endosome membranes leads to uncoating of the viral RNA segments into the cytoplasm.
Replication of viral RNA (vRNA) and transcription of mRNA takes place in the nucleus. Viral proteins are then transcribed in the cytoplasm,
viral particle is assembled near the cell membrane and released by budding.
Figure 1.3 Mechanism of viral fusion. (A) Pre-fusion conformation. (B) Proton binding of HA induces a conformational change exposing the
fusion peptide, which interacts with the endosome membrane bridging the two membranes together as an intermediate. (C) The intermediate
collapses, pulling the two membranes together. (D) An hemifusion diaphragm is formed, followed by a fusion pore (E), completing the fusion
process.