Page 64 - Canine Lameness
P. 64
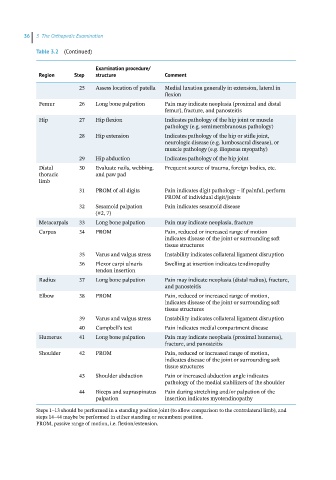
36 3 The Orthopedic Examination
Table 3.2 (Continued)
Examination procedure/
Region Step structure Comment
25 Assess location of patella Medial luxation generally in extension, lateral in
flexion
Femur 26 Long bone palpation Pain may indicate neoplasia (proximal and distal
femur), fracture, and panosteitis
Hip 27 Hip flexion Indicates pathology of the hip joint or muscle
pathology (e.g. semimembranosus pathology)
28 Hip extension Indicates pathology of the hip or stifle joint,
neurologic disease (e.g. lumbosacral disease), or
muscle pathology (e.g. iliopsoas myopathy)
29 Hip abduction Indicates pathology of the hip joint
Distal 30 Evaluate nails, webbing, Frequent source of trauma, foreign bodies, etc.
thoracic and paw pad
limb
31 PROM of all digits Pain indicates digit pathology – if painful, perform
PROM of individual digit/joints
32 Sesamoid palpation Pain indicates sesamoid disease
(#2, 7)
Metacarpals 33 Long bone palpation Pain may indicate neoplasia, fracture
Carpus 34 PROM Pain, reduced or increased range of motion
indicates disease of the joint or surrounding soft
tissue structures
35 Varus and valgus stress Instability indicates collateral ligament disruption
36 Flexor carpi ulnaris Swelling at insertion indicates tendinopathy
tendon insertion
Radius 37 Long bone palpation Pain may indicate neoplasia (distal radius), fracture,
and panosteitis
Elbow 38 PROM Pain, reduced or increased range of motion,
indicates disease of the joint or surrounding soft
tissue structures
39 Varus and valgus stress Instability indicates collateral ligament disruption
40 Campbell’s test Pain indicates medial compartment disease
Humerus 41 Long bone palpation Pain may indicate neoplasia (proximal humerus),
fracture, and panosteitis
Shoulder 42 PROM Pain, reduced or increased range of motion,
indicates disease of the joint or surrounding soft
tissue structures
43 Shoulder abduction Pain or increased abduction angle indicates
pathology of the medial stabilizers of the shoulder
44 Biceps and supraspinatus Pain during stretching and/or palpation of the
palpation insertion indicates myotendinopathy
Steps 1–13 should be performed in a standing position joint (to allow comparison to the contralateral limb), and
steps 14–44 maybe be performed in either standing or recumbent position.
PROM, passive range of motion, i.e. flexion/extension.