Page 162 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 162
130 Section 3 Cardiovascular Disease
Common Abnormal Cardiac Radiographic
VetBooks.ir Patterns
T4
Congenital and acquired heart diseases can be responsible
for generalized or localized cardiac enlargement associ-
ated with changes in the intrathoracic blood vessels. The
main cardiac causes responsible for left, right and global
heart enlargement are presented in Table 16.3 and in
Figures 16.7–16.12.
Left Heart Diseases (Figures 16.7–16.10)
Left Atrial Enlargement
On lateral views, left atrial enlargement is characterized by:
straightening of the dorsocaudal part of the cardiac
●
silhouette
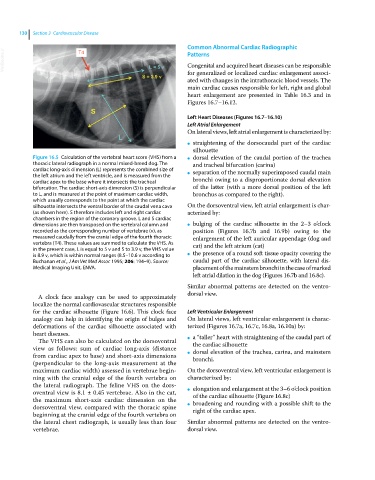
Figure 16.5 Calculation of the vertebral heart score (VHS) from a ● dorsal elevation of the caudal portion of the trachea
thoracic lateral radiograph in a normal mixed‐breed dog. The and tracheal bifurcation (carina)
cardiac long‐axis dimension (L) represents the combined size of separation of the normally superimposed caudal main
the left atrium and the left ventricle, and is measured from the ●
cardiac apex to the base where it intersects the tracheal bronchi owing to a disproportionate dorsal elevation
bifurcation. The cardiac short‐axis dimension (S) is perpendicular of the latter (with a more dorsal position of the left
to L, and is measured at the point of maximum cardiac width, bronchus as compared to the right).
which usually corresponds to the point at which the cardiac
silhouette intersects the ventral border of the caudal vena cava On the dorsoventral view, left atrial enlargement is char-
(as shown here). S therefore includes left and right cardiac acterized by:
chambers in the region of the coronary groove. L and S cardiac
dimensions are then transposed on the vertebral column and ● bulging of the cardiac silhouette in the 2–3 o’clock
recorded as the corresponding number of vertebrae (v), as position (Figures 16.7b and 16.9b) owing to the
measured caudally from the cranial edge of the fourth thoracic enlargement of the left auricular appendage (dog and
vertebra (T4). These values are summed to calculate the VHS. As cat) and the left atrium (cat)
in the present case, L is equal to 5 v and S to 3.9 v, the VHS value
is 8.9 v, which is within normal ranges (8.5–10.6 v according to ● the presence of a round soft tissue opacity covering the
Buchanan et al., J Am Vet Med Assoc 1995; 206: 194–9). Source: caudal part of the cardiac silhouette, with lateral dis-
Medical Imaging Unit, ENVA. placement of the mainstem bronchi in the case of marked
left atrial dilation in the dog (Figures 16.7b and 16.8c).
Similar abnormal patterns are detected on the ventro-
dorsal view.
A clock face analogy can be used to approximately
localize the normal cardiovascular structures responsible
for the cardiac silhouette (Figure 16.6). This clock face Left Ventricular Enlargement
analogy can help in identifying the origin of bulges and On lateral views, left ventricular enlargement is charac-
deformations of the cardiac silhouette associated with terized (Figures 16.7a, 16.7c, 16.8a, 16.10a) by:
heart diseases. a “taller” heart with straightening of the caudal part of
The VHS can also be calculated on the dorsoventral ● the cardiac silhouette
view as follows: sum of cardiac long‐axis (distance dorsal elevation of the trachea, carina, and mainstem
from cardiac apex to base) and short‐axis dimensions ● bronchi.
(perpendicular to the long‐axis measurement at the
maximum cardiac width) assessed in vertebrae begin- On the dorsoventral view, left ventricular enlargement is
ning with the cranial edge of the fourth vertebra on characterized by:
the lateral radiograph. The feline VHS on the dors- elongation and enlargement at the 3–6 o’clock position
oventral view is 8.1 ± 0.45 vertebrae. Also in the cat, ● of the cardiac silhouette (Figure 16.8c)
the maximum short‐axis cardiac dimension on the broadening and rounding with a possible shift to the
dorsoventral view, compared with the thoracic spine ● right of the cardiac apex.
beginning at the cranial edge of the fourth vertebra on
the lateral chest radiograph, is usually less than four Similar abnormal patterns are detected on the ventro-
vertebrae. dorsal view.