Page 157 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 157
15 Approach to the Patient with Suspected Cardiovascular Disease 125
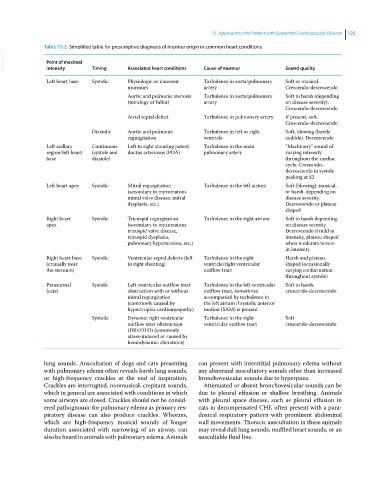
Table 15.2 Simplified table for presumptive diagnosis of murmur origin in common heart conditions
VetBooks.ir Point of maximal Timing Associated heart conditions Cause of murmur Sound quality
intensity
Left heart base Systolic Physiologic or innocent Turbulence in aorta/pulmonary Soft or musical.
murmurs artery Crescendo‐decrescendo
Aortic and pulmonic stenosis Turbulence in aorta/pulmonary Soft to harsh (depending
(tetralogy of Fallot) artery on disease severity).
Crescendo‐decrescendo
Atrial septal defect Turbulence in pulmonary artery If present, soft.
Crescendo‐decrescendo
Diastolic Aortic and pulmonic Turbulence in left or right Soft, blowing (barely
regurgitation ventricle audible). Decrescendo
Left axillary Continuous Left to right shunting patent Turbulence in the main “Machinery” sound of
region/left heart (systole and ductus arteriosus (PDA) pulmonary artery varying intensity
base diastole) throughout the cardiac
cycle. Crescendo‐
decrescendo in systole
peaking at S2
Left heart apex Systolic Mitral regurgitation Turbulence in the left atrium Soft (blowing), musical,
(secondary to myxomatous or harsh, depending on
mitral valve disease, mitral disease severity.
dysplasia, etc.) Decrescendo or plateau
shaped
Right heart Systolic Tricuspid regurgitation Turbulence in the right atrium Soft to harsh depending
apex (secondary to myxomatous on disease severity.
tricuspid valve disease, Decrescendo if mild in
tricuspid dysplasia, intensity, plateau shaped
pulmonary hypertension, etc.) when moderate/severe
in intensity
Right heart base Systolic Ventricular septal defects (left Turbulence in the right Harsh and plateau
(cranially near to right shunting) ventricle/right ventricular shaped (occasionally
the sternum) outflow tract varying conformation
throughout systole)
Parasternal Systolic Left ventricular outflow tract Turbulence in the left ventricular Soft to harsh,
(cats) obstruction with or without outflow tract, sometimes crescendo‐decrescendo
mitral regurgitation accompanied by turbulence in
(commonly caused by the left atrium if systolic anterior
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) motion (SAM) is present
Systolic Dynamic right ventricular Turbulence in the right Soft
outflow tract obstruction ventricular outflow tract crescendo‐decrescendo
(DRVOTO) (commonly
stress‐induced or caused by
hemodynamic alterations)
lung sounds. Auscultation of dogs and cats presenting can present with interstitial pulmonary edema without
with pulmonary edema often reveals harsh lung sounds, any abnormal auscultatory sounds other than increased
or high‐frequency crackles at the end of inspiration. bronchovesicular sounds due to hyperpnea.
Crackles are interrupted, nonmusical, crepitant sounds, Attenuated or absent bronchovesicular sounds can be
which in general are associated with conditions in which due to pleural effusion or shallow breathing. Animals
some airways are closed. Crackles should not be consid- with pleural space disease, such as pleural effusion in
ered pathognomic for pulmonary edema as primary res- cats in decompensated CHF, often present with a para-
piratory disease can also produce crackles. Wheezes, doxical respiratory pattern with prominent abdominal
which are high‐frequency musical sounds of longer wall movements. Thoracic auscultation in these animals
duration associated with narrowing of an airway, can may reveal dull lung sounds, muffled heart sounds, or an
also be heard in animals with pulmonary edema. Animals auscultable fluid line.