Page 172 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 172
140 Section 3 Cardiovascular Disease
direction and at approximately the same velocity through- the blood flow velocities in the selected sample gate are
VetBooks.ir out the entire cardiac cycle. Normal PW Doppler transval- very similar. Conversely, normal CW Doppler flow profiles
appear as completely filled because of the various velocities
vular flow profiles therefore appear as hollow
recorded all along the CW scan line (Figure 16.21b).
(Figures 16.21c, 16.21d, 16.22b, 16.22c, 16.23c), because
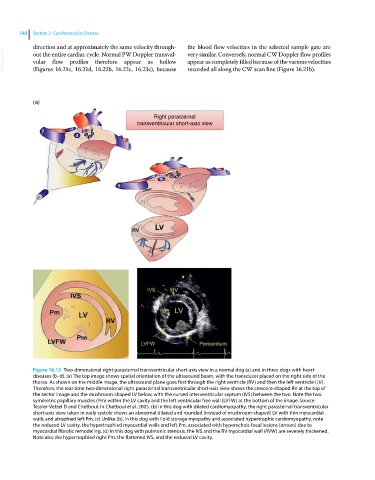
(a)
Right parasternal
transventricular short-axis view
Figure 16.13 Two‐dimensional right parasternal transventricular short‐axis view in a normal dog (a) and in three dogs with heart
diseases (b–d). (a) The top image shows spatial orientation of the ultrasound beam, with the transducer placed on the right side of the
thorax. As shown on the middle image, the ultrasound plane goes first through the right ventricle (RV) and then the left ventricle (LV).
Therefore, the real‐time two‐dimensional right parasternal transventricular short‐axis view shows the crescent‐shaped RV at the top of
the sector image and the mushroom‐shaped LV below, with the curved interventricular septum (IVS) between the two. Note the two
symmetric papillary muscles (Pm) within the LV cavity and the left ventricular free wall (LVFW) at the bottom of the image. Source:
Tessier-Vetzel D and Chetboul. In Chetboul et al. 2005. (b) In this dog with dilated cardiomyopathy, the right parasternal transventricular
short‐axis view taken in early systole shows an abnormal dilated and rounded (instead of mushroom‐shaped) LV with thin myocardial
walls and atrophied left Pm. (c) Unlike (b), in this dog with lipid storage myopathy and associated hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, note
the reduced LV cavity, the hypertrophied myocardial walls and left Pm, associated with hyperechoic focal lesions (arrows) due to
myocardial fibrotic remodeling. (d) In this dog with pulmonic stenosis, the IVS and the RV myocardial wall (RVW) are severely thickened.
Note also the hypertrophied right Pm, the flattened IVS, and the reduced LV cavity.