Page 174 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 174
142 Section 3 Cardiovascular Disease
VetBooks.ir transmitral short-axis view
Right parasternal
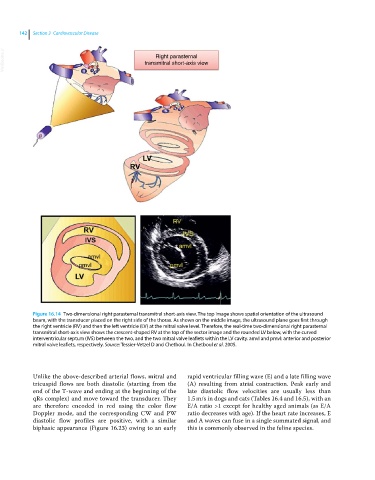
Figure 16.14 Two‐dimensional right parasternal transmitral short‐axis view. The top image shows spatial orientation of the ultrasound
beam, with the transducer placed on the right side of the thorax. As shown on the middle image, the ultrasound plane goes first through
the right ventricle (RV) and then the left ventricle (LV) at the mitral valve level. Therefore, the real‐time two‐dimensional right parasternal
transmitral short‐axis view shows the crescent‐shaped RV at the top of the sector image and the rounded LV below, with the curved
interventricular septum (IVS) between the two, and the two mitral valve leaflets within the LV cavity. amvl and pmvl: anterior and posterior
mitral valve leaflets, respectively. Source: Tessier-Vetzel D and Chetboul. In Chetboul et al. 2005.
Unlike the above‐described arterial flows, mitral and rapid ventricular filling wave (E) and a late filling wave
tricuspid flows are both diastolic (starting from the (A) resulting from atrial contraction. Peak early and
end of the T‐wave and ending at the beginning of the late diastolic flow velocities are usually less than
qRs complex) and move toward the transducer. They 1.5 m/s in dogs and cats (Tables 16.4 and 16.5), with an
are therefore encoded in red using the color flow E/A ratio >1 except for healthy aged animals (as E/A
Doppler mode, and the corresponding CW and PW ratio decreases with age). If the heart rate increases, E
diastolic flow profiles are positive, with a similar and A waves can fuse in a single summated signal, and
biphasic appearance (Figure 16.23) owing to an early this is commonly observed in the feline species.