Page 114 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 114
Minerals and Vitamins 115
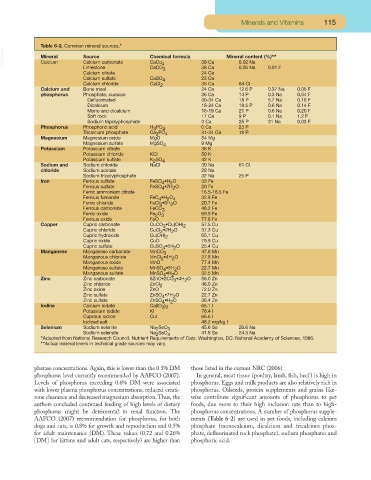
Table 6-2. Common mineral sources.*
VetBooks.ir Mineral Source Chemical formula 39 Ca Mineral content (%)**
Calcium
Calcium carbonate
CaCo
0.02 Na
4
Limestone
Calcium citrate CaCO 3 38 Ca 0.05 Na 0.01 F
24 Ca
Calcium sulfate CaSO 4 23 Ca
Calcium chloride CaCl 2 35 Ca 64 Cl
Calcium and Bone meal 24 Ca 12.6 P 0.37 Na 0.05 F
phosphorus Phosphate, curacao 36 Ca 14 P 0.3 Na 0.54 F
Defluorinated 30-34 Ca 18 P 5.7 Na 0.16 F
Dicalcium 18-24 Ca 18.5 P 0.6 Na 0.14 F
Mono and dicalcium 16-19 Ca 21 P 0.6 Na 0.20 F
Soft rock 17 Ca 9 P 0.1 Na 1.2 F
Sodium tripolyphosphate 0 Ca 25 P 31 Na 0.03 F
Phosphorus Phosphoric acid H PO 4 0 Ca 23 P
3
Tricalcium phosphate Ca PO 4 31-34 Ca 18 P
3
Magnesium Magnesium oxide MgO 54 Mg
Magnesium sulfate MgSO 4 9 Mg
Potassium Potassium citrate 36 K
Potassium chloride KCl 50 K
Potassium sulfate K SO 4 42 K
2
Sodium and Sodium chloride NaCl 39 Na 61 Cl
chloride Sodium acetate 28 Na
Sodium tripolyphosphate 32 Na 25 P
Iron Ferrous sulfate FeSO •H O 33 Fe
2
4
Ferrous sulfate FeSO •7H O 20 Fe
2
4
Ferric ammonium citrate 16.5-18.5 Fe
Ferrous fumarate FeC •H O 32.9 Fe
4
2 4
Ferric chloride FeCl •6H O 20.7 Fe
2
3
Ferrous carbonate FeCO 3 48.2 Fe
Ferric oxide Fe O 69.9 Fe
2 3
Ferrous oxide FeO 77.8 Fe
Copper Cupric carbonate CuCO •Cu(OH) 2 57.5 Cu
3
Cupric chloride CuCl •2H O 37.3 Cu
2
2
Cupric hydroxide Cu(OH) 2 65.1 Cu
Cupric oxide CuO 79.9 Cu
Cupric sulfate CuSO •5H O 25.4 Cu
2
4
Manganese Manganese carbonate MnCO 3 47.8 Mn
Manganous chloride MnCl •4H O 27.8 Mn
2
2
Manganous oxide MnO 77.4 Mn
Manganese sulfate MnSO •5H O 22.7 Mn
4
2
Manganous sulfate MnSO •H O 32.5 Mn
2
4
Zinc Zinc carbonate 5ZnO•2CO •4H O 56.0 Zn
2
3
Zinc chloride ZnCl 2 48.0 Zn
Zinc oxide ZnO 72.0 Zn
Zinc sulfate ZnSO •7H O 22.7 Zn
4
2
Zinc sulfate ZnSO •H O 36.4 Zn
2
4
Iodine Calcium iodate Ca(IO ) 65.1 I
3 2
Potassium iodide KI 76.4 I
Cuprous iodide CuI 66.6 I
Iodized salt 48.2 mg/kg I
Selenium Sodium selenite Na SeO 3 45.6 Se 26.6 Na
2
Sodium selenate Na SeO 4 41.8 Se 24.3 Na
2
*Adapted from National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Cats. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences, 1986.
**Actual mineral levels in technical grade sources may vary.
phatase concentrations. Again, this is lower than the 0.5% DM those listed in the current NRC (2006).
phosphorus level currently recommended by AAFCO (2007). In general, meat tissue (poultry, lamb, fish, beef) is high in
Levels of phosphorus exceeding 0.6% DM were associated phosphorus. Eggs and milk products are also relatively rich in
with lower plasma phosphorus concentrations, reduced creati- phosphorus. Oilseeds, protein supplements and grains like-
nine clearance and decreased magnesium absorption.Thus, the wise contribute significant amounts of phosphorus to pet
authors concluded continued feeding of high levels of dietary foods, due more to their high inclusion rate than to high-
phosphorus might be detrimental to renal function. The phosphorus concentrations. A number of phosphorus supple-
AAFCO (2007) recommendation for phosphorus, for both ments (Table 6-2) are used in pet foods, including calcium
dogs and cats, is 0.8% for growth and reproduction and 0.5% phosphate (monocalcium, dicalcium and tricalcium phos-
for adult maintenance (DM). These values (0.72 and 0.26% phate, defluorinated rock phosphate), sodium phosphates and
[DM] for kittens and adult cats, respectively) are higher than phosphoric acid.