Page 214 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 214
216 Small Animal Clinical Nutrition
5. Is a Source of Calcium and Other
Minerals Provided?
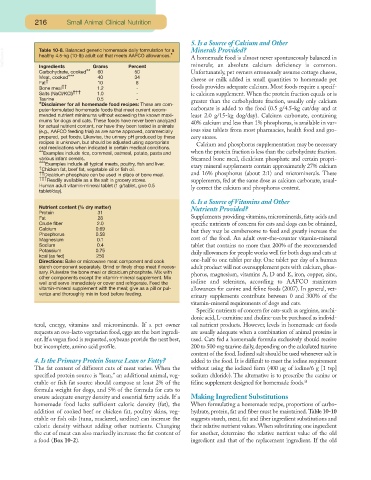
Table 10-8. Balanced generic homemade daily formulation for a
VetBooks.ir healthy 4.5-kg (10-lb) adult cat that meets AAFCO allowances.* A homemade food is almost never spontaneously balanced in
Ingredients
Carbohydrate, cooked** Grams Percent minerals; an absolute calcium deficiency is common.
Unfortunately, pet owners erroneously assume cottage cheese,
50
60
Meat, cooked*** 40 34 cheese or milk added in small quantities to homemade pet
Fat † 10 8
Bone meal †† 1.2 - foods provides adequate calcium. Most foods require a specif-
Salts (NaCl/KCl) ††† 1.0 - ic calcium supplement. When the protein fraction equals or is
Taurine 0.5 - greater than the carbohydrate fraction, usually only calcium
*Disclaimer for all homemade food recipes: These are com-
puter-formulated homemade foods that meet current recom- carbonate is added to the food (0.5 g/4.5-kg cat/day and at
mended nutrient minimums without exceeding the known maxi- least 2.0 g/15-kg dog/day). Calcium carbonate, containing
mums for dogs and cats. These foods have never been analyzed 40% calcium and less than 1% phosphorus, is available in var-
for actual nutrient content, nor have they been tested in animals
(e.g., AAFCO feeding trial) as are some approved, commercially ious size tablets from most pharmacies, health food and gro-
prepared, pet foods. Likewise, the urinary pH produced by these cery stores.
recipes is unknown, but should be adjusted using appropriate Calcium and phosphorus supplementation may be necessary
oral medications when indicated in certain medical conditions.
**Examples include rice, cornmeal, oatmeal, potato, pasta and when the protein fraction is less than the carbohydrate fraction.
various infant cereals. Steamed bone meal, dicalcium phosphate and certain propri-
***Examples include all typical meats, poultry, fish and liver.
† Chicken fat, beef fat, vegetable oil or fish oil. etary mineral supplements contain approximately 27% calcium
†† Dicalcium phosphate can be used in place of bone meal. and 16% phosphorus (about 2:1) and microminerals. These
††† Readily available as a lite salt in grocery stores. supplements, fed at the same dose as calcium carbonate, usual-
Human adult vitamin-mineral tablet (1 g/tablet, give 0.5 ly correct the calcium and phosphorus content.
tablet/day).
6. Is a Source of Vitamins and Other
Nutrient content (% dry matter) Nutrients Provided?
Protein 31
Fat 28 Supplements providing vitamins,microminerals,fatty acids and
Crude fiber 2.0 specific nutrients of concern for cats and dogs can be obtained,
Calcium 0.69 but they may be cumbersome to feed and greatly increase the
Phosphorus 0.58
Magnesium 0.1 cost of the food. An adult over-the-counter vitamin-mineral
Sodium 0.4 tablet that contains no more than 200% of the recommended
Potassium 0.75 daily allowances for people works well for both dogs and cats at
kcal (as fed) 250
Directions: Bake or microwave meat component and cook one-half to one tablet per day. One tablet per day of a human
starch component separately. Grind or finely chop meat if neces- adult product will not oversupplement pets with calcium, phos-
sary. Pulverize the bone meal or dicalcium phosphate. Mix with phorus, magnesium, vitamins A, D and E, iron, copper, zinc,
other components except the vitamin-mineral supplement. Mix
well and serve immediately or cover and refrigerate. Feed the iodine and selenium, according to AAFCO maximum
vitamin-mineral supplement with the meal; give as a pill or pul- allowances for canine and feline foods (2007). In general, vet-
verize and thoroughly mix in food before feeding.
erinary supplements contribute between 0 and 300% of the
vitamin-mineral requirements of dogs and cats.
Specific nutrients of concern for cats-such as arginine, arachi-
donic acid,L-carnitine and choline-can be purchased as individ-
terol, energy, vitamins and microminerals. If a pet owner ual nutrient products. However, levels in homemade cat foods
requests an ovo-lacto vegetarian food, eggs are the best ingredi- are usually adequate when a combination of animal proteins is
ent. If a vegan food is requested, soybeans provide the next best, used. Cats fed a homemade formula exclusively should receive
but incomplete, amino acid profile. 200 to 500 mg taurine daily,depending on the calculated taurine
content of the food. Iodized salt should be used whenever salt is
4. Is the Primary Protein Source Lean or Fatty? added to the food. It is difficult to meet the iodine requirement
The fat content of different cuts of meat varies. When the without using the iodized form (400 µg of iodine/6 g [1 tsp]
specified protein source is “lean,” an additional animal, veg- sodium chloride). The alternative is to prescribe the canine or
etable or fish fat source should compose at least 2% of the feline supplement designed for homemade foods. a
formula weight for dogs, and 5% of the formula for cats to
ensure adequate energy density and essential fatty acids. If a Making Ingredient Substitutions
homemade food lacks sufficient caloric density (fat), the When formulating a homemade recipe, proportions of carbo-
addition of cooked beef or chicken fat, poultry skins, veg- hydrate, protein, fat and fiber must be maintained. Table 10-10
etable or fish oils (tuna, mackerel, sardine) can increase the suggests starch, meat, fat and fiber ingredient substitutions and
caloric density without adding other nutrients. Changing their relative nutrient values. When substituting one ingredient
the cut of meat can also markedly increase the fat content of for another, determine the relative nutrient value of the old
a food (Box 10-2). ingredient and that of the replacement ingredient. If the old