Page 1416 - Saunders Comprehensive Review For NCLEX-RN
P. 1416
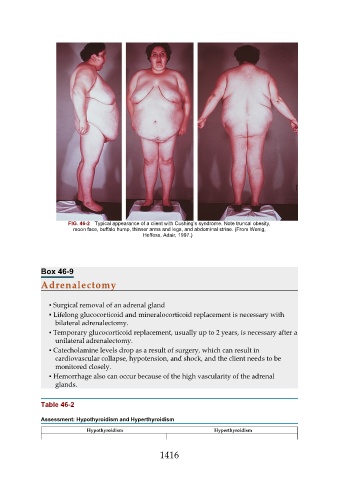
FIG. 46-2 Typical appearance of a client with Cushing’s syndrome. Note truncal obesity,
moon face, buffalo hump, thinner arms and legs, and abdominal striae. (From Wenig,
Heffess, Adair, 1997.)
Box 46-9
Adrenalectomy
▪ Surgical removal of an adrenal gland
▪ Lifelong glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid replacement is necessary with
bilateral adrenalectomy.
▪ Temporary glucocorticoid replacement, usually up to 2 years, is necessary after a
unilateral adrenalectomy.
▪ Catecholamine levels drop as a result of surgery, which can result in
cardiovascular collapse, hypotension, and shock, and the client needs to be
monitored closely.
▪ Hemorrhage also can occur because of the high vascularity of the adrenal
glands.
Table 46-2
Assessment: Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism
1416