Page 1550 - Saunders Comprehensive Review For NCLEX-RN
P. 1550
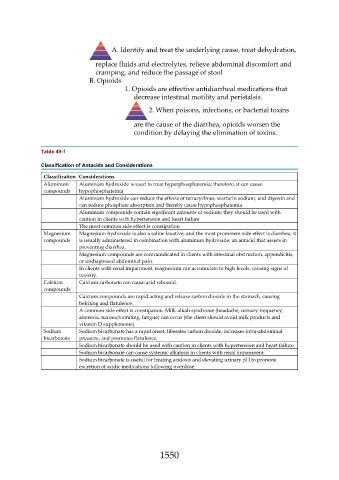
A. Identify and treat the underlying cause, treat dehydration,
replace fluids and electrolytes, relieve abdominal discomfort and
cramping, and reduce the passage of stool
B. Opioids
1. Opioids are effective antidiarrheal medications that
decrease intestinal motility and peristalsis.
2. When poisons, infections, or bacterial toxins
are the cause of the diarrhea, opioids worsen the
condition by delaying the elimination of toxins.
Table 49-1
Classification of Antacids and Considerations
Classification Considerations
Aluminum Aluminum hydroxide is used to treat hyperphosphatemia; therefore, it can cause
compounds hypophosphatemia
Aluminum hydroxide can reduce the effects of tetracyclines, warfarin sodium, and digoxin and
can reduce phosphate absorption and thereby cause hypophosphatemia
Aluminum compounds contain significant amounts of sodium; they should be used with
caution in clients with hypertension and heart failure
The most common side effect is constipation
Magnesium Magnesium hydroxide is also a saline laxative, and the most prominent side effect is diarrhea; it
compounds is usually administered in combination with aluminum hydroxide, an antacid that assists in
preventing diarrhea.
Magnesium compounds are contraindicated in clients with intestinal obstruction, appendicitis,
or undiagnosed abdominal pain.
In clients with renal impairment, magnesium can accumulate to high levels, causing signs of
toxicity.
Calcium Calcium carbonate can cause acid rebound.
compounds
Calcium compounds are rapid acting and release carbon dioxide in the stomach, causing
belching and flatulence.
A common side effect is constipation. Milk-alkali syndrome (headache, urinary frequency,
anorexia, nausea/vomiting, fatigue) can occur (the client should avoid milk products and
vitamin D supplements)
Sodium Sodium bicarbonate has a rapid onset, liberates carbon dioxide, increases intra-abdominal
bicarbonate pressure, and promotes flatulence.
Sodium bicarbonate should be used with caution in clients with hypertension and heart failure.
Sodium bicarbonate can cause systemic alkalosis in clients with renal impairment.
Sodium bicarbonate is useful for treating acidosis and elevating urinary pH to promote
excretion of acidic medications following overdose.
1550