Page 662 - Saunders Comprehensive Review For NCLEX-RN
P. 662
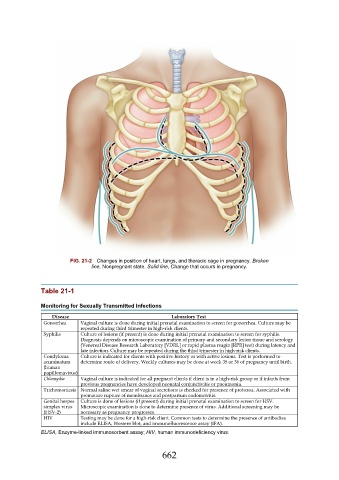
FIG. 21-2 Changes in position of heart, lungs, and thoracic cage in pregnancy. Broken
line, Nonpregnant state. Solid line, Change that occurs in pregnancy.
Table 21-1
Monitoring for Sexually Transmitted Infections
Disease Laboratory Test
Gonorrhea Vaginal culture is done during initial prenatal examination to screen for gonorrhea. Culture may be
repeated during third trimester in high-risk clients.
Syphilis Culture of lesions (if present) is done during initial prenatal examination to screen for syphilis.
Diagnosis depends on microscopic examination of primary and secondary lesion tissue and serology
(Venereal Disease Research Laboratory [VDRL] or rapid plasma reagin [RPR] test) during latency and
late infection. Culture may be repeated during the third trimester in high-risk clients.
Condyloma Culture is indicated for clients with positive history or with active lesions. Test is performed to
acuminatum determine route of delivery. Weekly cultures may be done at week 35 or 36 of pregnancy until birth.
(human
papillomavirus)
Chlamydia Vaginal culture is indicated for all pregnant clients if client is in a high-risk group or if infants from
previous pregnancies have developed neonatal conjunctivitis or pneumonia.
Trichomoniasis Normal saline wet smear of vaginal secretions is checked for presence of protozoa. Associated with
premature rupture of membranes and postpartum endometritis.
Genital herpes Culture is done of lesions (if present) during initial prenatal examination to screen for HSV.
simplex virus Microscopic examination is done to determine presence of virus. Additional screening may be
(HSV-2) necessary as pregnancy progresses.
HIV Testing may be done for a high-risk client. Common tests to determine the presence of antibodies
include ELISA, Western blot, and immunofluorescence assay (IFA).
ELISA, Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
662