Page 22 - Math SL HB Sem 3
P. 22
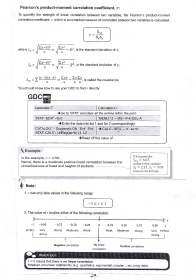
Pearson's product-moment correlation coefficient, r:
To quantify the strength of linear correlation between two variables, the Pearson's product-moment
correlation coefficient, r, which is a numerical measure of correlation between two variables is calculated.
S,,
SrSy
,(x-I\2 E"
where Sr = - i, , is the standard deviation of a:
n ,1
,o-D2
n '{ - f ,is the standard deviation of y;
(x-r)(y-t)
c Zxy ExZy
-T = ="':- - is called the covariance
nltLfl --,
You should know how to use your cDC to flnd r directly:
GDC
Calculator-T: Calculator-C:
tGo to 'STAT'and ciear all the entries left in the past:
,STAT'-'EDIT' 'ueru'-'z'
-ENt' ->F4)'DEL-A
| - 1ro
,Enter the data into list 1 and list 2 correspondingly
'CATALOG' '-' Diagnostic ON -'Ent' -Ent' )'CALC'-'REG' -'X'-'ax+b'
'STAT'-CALC'- LinReg(ax+b) L1 , L2
tRead off the value of
\ Example:
If it is given that
ln the example, r = 0.701.
S,v = 8'67'
Hence, there is a moderate positive linear conelation between the
b findr, first calculate:
circumferences of head and heights of students Sr=2.11,Sy=5.85
then use the formula.
t:
l! Note:
'
,. , nonly take values in the following range:
"
r
1 1
2. The value of r implies either of the following correlation
-1 -0.90 -0.75 -0.50 -0.2s 0 0.25 0.50 0.75 0.90 1
Perfect Strong Moderate Moderate Strong Perfect
strong strong
Negative correla6on No linear
Positive correlation
correlation
Watch Out:
r = 0 means that there is no linear correlation.
However, non-linear relationship (e.g, quadratics, exponential, circular... etc.) may exist
*t-