Page 39 - Math SL HB Sem 3
P. 39
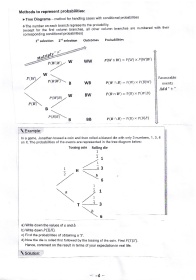
Methods to represent probabilities:
>Tree Diagrams - method for handling cases with conditional probabilities
*The number on each branch represents the probability'
(except for the first column Oiincnes, all other column branches are numbered with their
corresponding conditional probabilities)
li selection Znd selection outcomes Probabilities
x'
W WW P(w nw): P(w) x P(wlw)
W
P( Favourable
P(BI wB P(w) x P(Bl!12)
B P(w B) = events
^
Add" +"
W BW P(B = P(B) x P(,'lzlB)
P(wlB) ^w)
P(B
B
P(BlB)
B BB P(B N B): P(B) X P(BIB)
\. Exa mple:
ln a game, Jonathan tossed a coin and then rolled a biased die with only 3 numbers, 1, 3, 6
on it. The probabilities of the events are represented in the tree diagram below:
Tossing coin Rolli ng die
7
;
1
1
1 H 3
,
b
6
4
o 1 L
T 3
\ 6
a) Write down lhe values of a and b.
b) Write down P(3lH).
c) Find the probabililies of obtaining a '3'.
pOl3').
d) Now the die is rolled first followed by the tossing of the coin. Find
Hence, comment on the result in terms of your expectation in real life.
4