Page 62 - Math SL HB Sem 3
P. 62
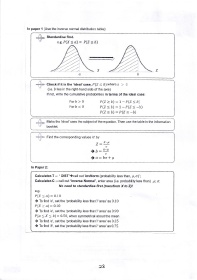
ln paper 1 (Use the inverse normal distribution table):
+ Standardise first.
e.g. P(X < a) : P(Z < b)
X Z
a b
-.
-,/
..=.p- Check if it is the 'ideal' case, P(Z < b) wherc b > 0
(i.e. b lies in the right-hand side of the axis)
lf not, write the cumulative probabilities in terms of the ideal case:
Forb ) 0 P(Z>b):7-P(Z<b)
1 P(Z <
Forb < 0 P(Z < b\ = - -h\
P(z>b)-P(z<-b)
S- Make the 'ideal' case the subject of the equation. Then use the table in the information
booklet.
++:€. Find the conesponding values h' by
- x-tt
t
) b _9:-L
o
,a-bo+lt
ln Paper 2:
Calculator-T - 'DIST')call out'invNorm (probability less than, p, o)';
Calculator-C - call out 'lnverse Normal', enter area (i.e. probability less than) , p, o;
No need to standardise first (tansform X to Z)!
e.g.
P(x<a)=o.ro
I To find 'o', set the 'probability less than'/'area'as 0.10
P(X > a) = 0.lg
) To find 'a', set the 'probability less than'/'area'as 0.90
P(a < X < b) = 0.50, when symmetrical about the mean
) To find 'a', set the 'probability less than'/'area'as 0.25
t To find 'b', set the 'probability less than'/ 'area' as 0.75
23