Page 10 - Heart Transplant Protocol
P. 10
Heart Function Service: Heart Transplant Protocols
Pre-Transplant Nutrition Assessment
Assess patient’s nutritional status.
Monitor both early and long-term nutritional intake and status to promote healing,
manage weight, and meet the body’s requirements.
Recommend dietary intervention to maximize pre-transplant nutritional status.
Educate the family regarding potential nutritional risks, negative outcomes associated
with poor nutrition, and interventions that support long-term transplant success and
optimal health.
Pre-Transplant Financial Assessment
Completion of a financial screening.
Review medical, as well as current pharmacy benefits.
Discuss the importance of maintaining active coverage and advising on coverage
changes.
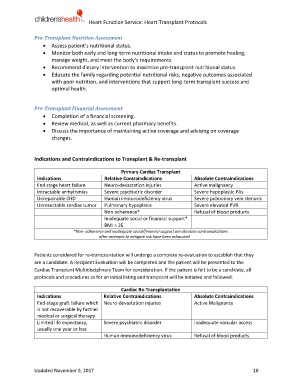
Indications and Contraindications to Transplant & Re-transplant
Primary Cardiac Transplant
Indications Relative Contraindications Absolute Contraindications
End stage heart failure Neuro-devastation injuries Active malignancy
Intractable arrhythmias Severe psychiatric disorder Severe hypoplastic PAs
Unrepairable CHD Human immunodeficiency virus Severe pulmonary vein stenosis
Unresectable cardiac tumor Pulmonary hypoplasia Severe elevated PVR
Non adherence* Refusal of blood products
Inadequate social or financial support*
BMI > 35
*Non- adherence and inadequate social/financial support are absolute contraindications
after attempts to mitigate risk have been exhausted
Patients considered for re-transplantation will undergo a complete re-evaluation to establish that they
are a candidate. A Recipient Evaluation will be completed and the patient will be presented to the
Cardiac Transplant Multidisciplinary Team for consideration. If the patient is felt to be a candidate, all
protocols and procedures as for an initial listing and transplant will be initiated and followed.
Cardiac Re-Transplantation
Indications Relative Contraindications Absolute Contraindications
End-stage graft failure which Neuro-devastation injuries Active Malignancy
is not recoverable by further
medical or surgical therapy.
Limited life expectancy, Severe psychiatric disorder Inadequate vascular access
usually one year or less
Human immunodeficiency virus Refusal of blood products
Updated November 9, 2017 10