Page 136 - Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
P. 136
124 Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
34. What are the clinical features of mitral stenosis?
Table 6: Clinical features of mitral stenosis
• Dyspnea, palpitations, hemoptysis, bronchitis, etc.
History • Peripheral edema in late stages due to right heart
failure
Pulse • Small volume pulse; often irregular due to AF
• Undisplaced and tapping apical impulse
Precordial • Diastolic apical thrill
impulses • Left parasternal heave if there is right ventricular
hypertrophy
• Loud S1
• Opening snap (high-pitched sound just medial to the
Heart apex)
sounds
• Loud P2 in pulmonary area in pulmonary arterial
hypertension
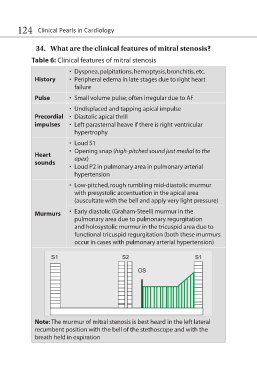
• Low-pitched, rough rumbling mid-diastolic murmur
with presystolic accentuation in the apical area
(auscultate with the bell and apply very light pressure)
Murmurs • Early diastolic (Graham-Steell) murmur in the
pulmonary area due to pulmonary regurgitation
and holosystolic murmur in the tricuspid area due to
functional tricuspid regurgitation (both these murmurs
occur in cases with pulmonary arterial hypertension)
Note: The murmur of mitral stenosis is best heard in the left lateral
recumbent position with the bell of the stethoscope and with the
breath held in expiration