Page 138 - Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
P. 138
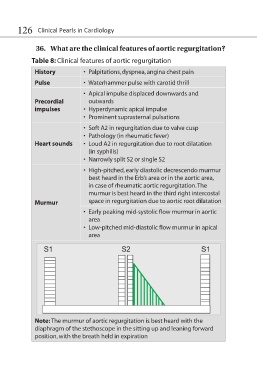
126 Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
36. What are the clinical features of aortic regurgitation?
Table 8: Clinical features of aortic regurgitation
History • Palpitations, dyspnea, angina chest pain
Pulse • Waterhammer pulse with carotid thrill
• Apical impulse displaced downwards and
Precordial outwards
impulses • Hyperdynamic apical impulse
• Prominent suprasternal pulsations
• Soft A2 in regurgitation due to valve cusp
• Pathology (in rheumatic fever)
Heart sounds • Loud A2 in regurgitation due to root dilatation
(in syphilis)
• Narrowly split S2 or single S2
• High-pitched, early diastolic decrescendo murmur
best heard in the Erb’s area or in the aortic area,
in case of rheumatic aortic regurgitation. The
murmur is best heard in the third right intercostal
Murmur space in regurgitation due to aortic root dilatation
• Early peaking mid-systolic flow murmur in aortic
area
• Low-pitched mid-diastolic flow murmur in apical
area
Note: The murmur of aortic regurgitation is best heard with the
diaphragm of the stethoscope in the sitting up and leaning forward
position, with the breath held in expiration