Page 45 - Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
P. 45
Arterial Pulse and Blood Pressure 33
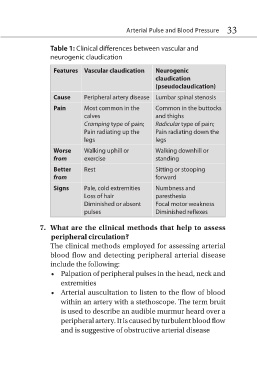
Table 1: Clinical differences between vascular and
neurogenic claudication
Features Vascular claudication Neurogenic
claudication
(pseudoclaudication)
Cause Peripheral artery disease Lumbar spinal stenosis
Pain Most common in the Common in the buttocks
calves and thighs
Cramping type of pain; Radicular type of pain;
Pain radiating up the Pain radiating down the
legs legs
Worse Walking uphill or Walking downhill or
from exercise standing
Better Rest Sitting or stooping
from forward
Signs Pale, cold extremities Numbness and
Loss of hair paresthesia
Diminished or absent Focal motor weakness
pulses Diminished reflexes
7. What are the clinical methods that help to assess
peripheral circulation?
The clinical methods employed for assessing arterial
blood flow and detecting peripheral arterial disease
include the following:
• Palpation of peripheral pulses in the head, neck and
extremities
• Arterial auscultation to listen to the flow of blood
within an artery with a stethoscope. The term bruit
is used to describe an audible murmur heard over a
peripheral artery. It is caused by turbulent blood flow
and is suggestive of obstructive arterial disease