Page 47 - Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
P. 47
Arterial Pulse and Blood Pressure 35
manifestations of chronic limb ischemia. Chronic limb
ischemia can also result in the formation of punched
out ulcers in the lower limbs. These ischemic ulcers are
usually located distal to the medial malleolus, on the
dorsum of the foot and toes (unlike venous ulcers which
are located proximal to the medial malleolus).
10. What is the relationship between pulse pressure,
arterial pulse volume and rate of upstroke of arterial
pulse?
The volume or amplitude of the arterial pulse is assessed
by determining the displacement felt by the palpating
fingers. The displacement is dependent on the change
in tension developed in the arterial wall during diastole
and systole (i.e the displacement or pulse volume is
dependent on the difference between systolic and
diastolic blood pressure). Thus the volume of arterial
pulse is directly proportional to the pulse pressure. The
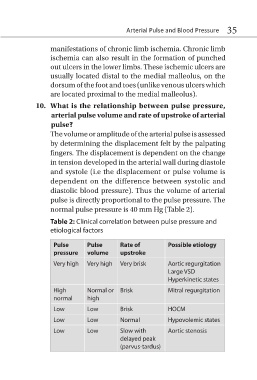
normal pulse pressure is 40 mm Hg (Table 2).
Table 2: Clinical correlation between pulse pressure and
etiological factors
Pulse Pulse Rate of Possible etiology
pressure volume upstroke
Very high Very high Very brisk Aortic regurgitation
Large VSD
Hyperkinetic states
High Normal or Brisk Mitral regurgitation
normal high
Low Low Brisk HOCM
Low Low Normal Hypovolemic states
Low Low Slow with Aortic stenosis
delayed peak
(parvus-tardus)