Page 246 - Chemistry
P. 246
b) Pressure increase, and favours backward reaction √ ½ which is at lower pressure; hence
equilibrium shifts to the right. √ ½
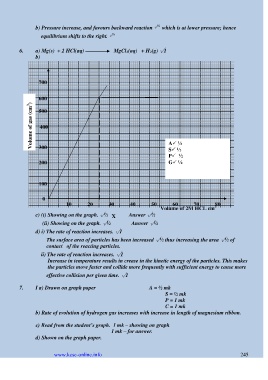
6. a) Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) MgCl 2(aq) + H 2(g) √1
b)
700
0
600
0
500
0
Volume of gas (cm 3 ) 400
300 A ½
S ½
P ½
200 G ½
100
0
60
80
70
10 20 30 40 50 Volume of 2M HCL cm
3
c) (i) Showing on the graph. √½ X Answer √½
(ii) Showing on the graph. √½ Answer √½
d) i) The rate of reaction increases. √1
The surface area of particles has been increased √½ thus increasing the area √½ of
contact of the reacting particles.
ii) The rate of reaction increases. √1
Increase in temperature results in crease in the kinetic energy of the particles. This makes
the particles move faster and collide more frequently with sufficient energy to cause more
effective collision per given time. √1
7. I a) Drawn on graph paper A = ½ mk
S = ½ mk
P = 1 mk
C = 1 mk
b) Rate of evolution of hydrogen gas increases with increase in length of magnesium ribbon.
c) Read from the student‟s graph. 1 mk – showing on graph
1 mk – for answer.
d) Shown on the graph paper.
www.kcse-online.info 245