Page 98 - Chemistry
P. 98
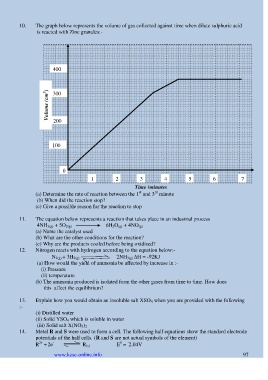
10. The graph below represents the volume of gas collected against time when dilute sulphuric acid
is reacted with Zinc granules:-
400
300
Volume (cm 3 )
200
100
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Time (minutes
rd
st
(a) Determine the rate of reaction between the 1 and 3 minute
(b) When did the reaction stop?
(c) Give a possible reason for the reaction to stop
11. The equation below represents a reaction that takes place in an industrial process
4NH 3(g) + 5O 2(g) 6H 2O (g) + 4NO (g)
(a) Name the catalyst used
(b) What are the other conditions for the reaction?
(c) Why are the products cooled before being oxidised?
12. Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen according to the equation below:-
N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) 2NH 3(g) H = -92KJ
(a) How would the yield of ammonia be affected by increase in :-
(i) Pressure
(ii) temperature
(b) The ammonia produced is isolated form the other gases from time to time. How does
this affect the equilibrium?
13. Explain how you would obtain an insoluble salt XSO 4 when you are provided with the following
:-
(i) Distilled water
(ii) Solid YSO 4 which is soluble in water
(iii) Solid salt X(NO 3) 2
14. Metal R and S were used to form a cell. The following half equations show the standard electrode
potentials of the half cells. (R and S are not actual symbols of the element)
-
2+
-
R + 2e R (s) E = 2.04V
www.kcse-online.info 97