Page 21 - GP Fall 2025
P. 21
Can We Trust and Use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to
Summarize Evidence?
Authors: Barret Towns and Analia Veitz-Keenan, DDS, FAGD
Background
Synthesizing evidence can take time, and practitioners need the evidence for clinical practice. Artificial intelligence (AI) can help with this
1
task, and it was used as an example for this review. The purpose of this review is to analyze the current evidence provided by systematic
2
reviews on patient compliance with orthodontic retainers. ChatGPT4o was used to assist in the search and analysis of the evidence.
Post-orthodontic retention is essential for maintaining treatment outcomes, yet long-term patient compliance with retainer wear remains
inconsistent. General practitioners encounter many patients who use or plan to undergo orthodontic treatment, and long-term treatment
success seems highly associated with utilizing a retention method. 3
This review aims to synthesize findings from four recent systematic and scoping reviews examining adherence to retainer protocols,
associated influencing factors, and strategies to improve compliance.
Methodology
ChatGPT4o was provided with the prompt to search for published evidence about this topic.
This narrative review consolidates evidence from four published systematic or scoping reviews between 2017 and 2024. These reviews
included 12 to 60 studies each, encompassing various patient populations and appliance types. Inclusion criteria focused on patient
adherence with removable orthodontic retainers, as measured through objective data, self-reports, and outcomes following educational or
digital intervention.
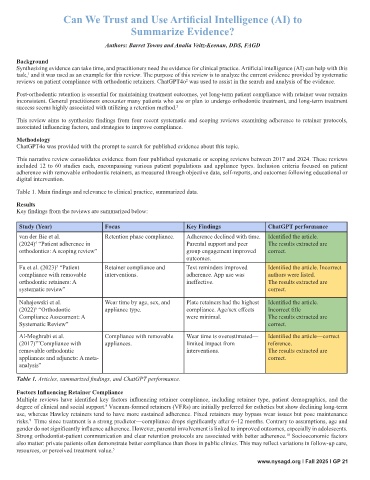
Table 1. Main findings and relevance to clinical practice, summarized data.
Results
Key findings from the reviews are summarized below:
Study (Year) Focus Key Findings ChatGPT performance
van der Bie et al. Retention phase compliance. Adherence declined with time. Identified the article.
(2024) “Patient adherence in Parental support and peer The results extracted are
4
orthodontics: A scoping review” group engagement improved correct.
outcomes.
Fu et al. (2023) “Patient Retainer compliance and Text reminders improved Identified the article. Incorrect
5
compliance with removable interventions. adherence. App use was authors were listed.
orthodontic retainers: A ineffective. The results extracted are
systematic review” correct.
Nahajowski et al. Wear time by age, sex, and Plate retainers had the highest Identified the article.
(2022) “Orthodontic appliance type. compliance. Age/sex effects Incorrect title
6
Compliance Assessment: A were minimal. The results extracted are
Systematic Review” correct.
Al-Moghrabi et al. Compliance with removable Wear time is overestimated— Identified the article—correct
(2017) ”Compliance with appliances. limited impact from reference.
7
removable orthodontic interventions. The results extracted are
appliances and adjuncts: A meta- correct.
analysis”
Table 1. Articles, summarized findings, and ChatGPT performance.
Factors Influencing Retainer Compliance
Multiple reviews have identified key factors influencing retainer compliance, including retainer type, patient demographics, and the
degree of clinical and social support. Vacuum-formed retainers (VFRs) are initially preferred for esthetics but show declining long-term
8
use, whereas Hawley retainers tend to have more sustained adherence. Fixed retainers may bypass wear issues but pose maintenance
risks. Time since treatment is a strong predictor—compliance drops significantly after 6–12 months. Contrary to assumptions, age and
9
gender do not significantly influence adherence. However, parental involvement is linked to improved outcomes, especially in adolescents.
Strong orthodontist-patient communication and clear retention protocols are associated with better adherence. Socioeconomic factors
10
also matter: private patients often demonstrate better compliance than those in public clinics. This may reflect variations in follow-up care,
resources, or perceived treatment value. 5
www.nysagd.org l Fall 2025 l GP 21