Page 257 - Microsoft Word - LessonPlan-Overview.doc
P. 257
and food moved into the waiting The amoeba is a common example
protist. of this type of protozoan.
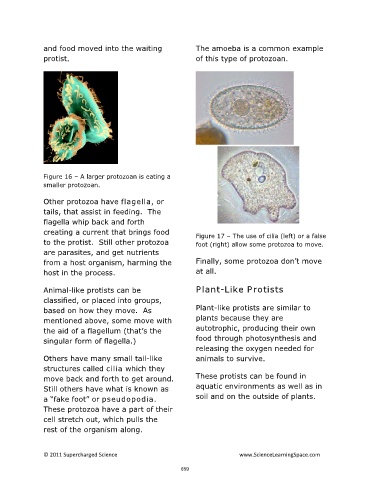
Figure 16 – A larger protozoan is eating a
smaller protozoan.
Other protozoa have flagella, or
tails, that assist in feeding. The
flagella whip back and forth
creating a current that brings food Figure 17 – The use of cilia (left) or a false
to the protist. Still other protozoa foot (right) allow some protozoa to move.
are parasites, and get nutrients
from a host organism, harming the Finally, some protozoa don’t move
host in the process. at all.
Animal-like protists can be Plant-Like Protists
classified, or placed into groups,
based on how they move. As Plant-like protists are similar to
mentioned above, some move with plants because they are
the aid of a flagellum (that’s the autotrophic, producing their own
singular form of flagella.) food through photosynthesis and
releasing the oxygen needed for
Others have many small tail-like animals to survive.
structures called cilia which they
move back and forth to get around. These protists can be found in
Still others have what is known as aquatic environments as well as in
a “fake foot” or pseudopodia. soil and on the outside of plants.
These protozoa have a part of their
cell stretch out, which pulls the
rest of the organism along.
© 2011 Supercharged Science www.ScienceLearningSpace.com
659