Page 68 - CHIRP Annual Digest 2017
P. 68
CHIRP Maritime
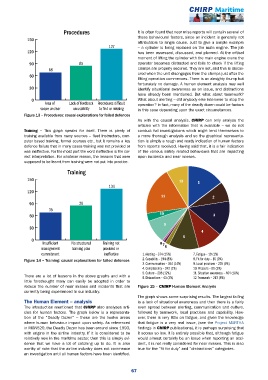
Procedures It is often found that near miss reports will contain several of
these behavioural factors, since an incident is generally not
150
11 1 attributable to single cause. Just to give a simple example
127 – a cylinder is being replaced on the main engine. The job
120 2 has been assessed, discussed, and planned. At the critical
10
moment of lifting the cylinder with the main engine crane the
90 85 operator becomes distracted and fails to check if the lifting
68 3 clamps are properly secured. They are not, and this is discov-
60 ered when the unit disengages from the clamps just after the
9 lifting operation commences. There is an almighty thump but
fortunately no damage. A human element analysis may well
30 identify situational awareness as an issue, and distractions
4
8 have already been mentioned. But what about teamwork?
0 What about alerting – did anybody else intervene to stop the
5
Area of 7 Lack of feedback Procedures dif
cult operation? In fact, many of the deadly dozen could be factors
6
scope unclear on usability to
nd or missing in this case depending upon the exact circumstances.
Figure 13 – Procedures: causal explanations for failed defences
As with the causal analysis, CHIRP can only analyse the
articles with the information that is available – we do not
Training – This graph speaks for itself. There is plenty of conduct full investigations which might lend themselves to
training available from many sources – fleet instructors, com- a more thorough analysis and so the graphical representa-
puter based training, formal courses etc., but it remains a key tion is simply a rough and ready indication of human factors
defence failure that in many cases training was not provided or from reports received. Having said that, it is a fair indication
was ineffective. For the most part the word ineffective is the cor- of the various safety related behaviours that are impacting
rect interpretation. For whatever reason, the lessons that were upon incidents and near misses.
supposed to be learnt from training were not put into practice.
Training
150
11 1 12 1
134
120 2
10 11 2
90 29
35 3
60 10 3
9
9
30
4 4
8 5
0
5
Insufcient 7 No structured Training not 8 7
6
management training plan provided or 6
commitment ineffective 1. Alerting – 374 (15%) 7. Fatigue – 19 (1%)
Figure 14 – Training: causal explanations for failed defences 2. Capability – 194 (8%) 8. Fit for duty – 16 (0%)
3. Communication – 344 (14%) 9. Local practices – 225 (9%)
4. Complacency – 242 (1%) 10. Pressure – 81 (3%)
5. Culture – 296 (12%) 11. Situation awareness – 464 (18%)
There are a lot of lessons in the above graphs and with a 6. Distractions – 43 (2%) 12. Teamwork – 213 (8%)
little forethought many can easily be adopted in order to
reduce the number of near misses and incidents that are Figure 15 – CHIRP Human Element Analysis
currently being experienced in our industry.
The graph shows some surprising results. The largest failing
The Human Element – analysis is a lack of situational awareness and then there is a fairly
The introduction mentioned that CHIRP also analyses arti- even spread between alerting, communication and culture,
cles for human factors. The graph below is a representa- followed by teamwork, local practices and capability. How-
tion of the “Deadly Dozen” – these are the twelve areas ever, there is very little on fatigue, and given the knowledge
where human behaviour impact upon safety. As referenced that fatigue is a very real issue, (see the Project MARTHA
in MGN520, the Deadly Dozen has been around since 1993, findings in CHIRP publications), it is perhaps surprising that
with origins in the airline industry. If it is considered to be it scores so low. It is entirely possible that, although fatigue
relatively new in the maritime sector, then this is simply evi- would almost certainly be an issue when reporting an acci-
dence that we have a lot of catching up to do. It is also dent, it is not really considered for near misses. This is also
worthy of note that the airline industry does not commence true for the “fit for duty” and “distractions” categories.
an investigation until all human factors have been identified.
67