Page 3 - Davis-Monthan AFB Desert Lightning News 6-12-15
P. 3
Desert Lightning News June 12, 2015 3
From WATER, Page 2 www.aerotechnews.com/davis-monthanafb
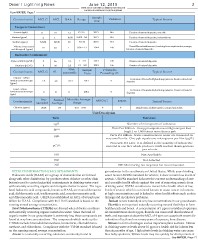
Contaminants MCLG MCL Facebook.com/DesertLightningNews
RAA Range Sample Violation Typical Source
Year
Inorganic Contaminant
Arsenic (ppb) 0 10 2.2 1.2-2.6 2013 No Erosion of natural deposits, run offs
2 2 0.061 0.050 - 0.0 2013 No
Barium (ppm) MNR MNR 30 30-32 2013 NA Erosion of natural deposits, industrial use
Erosion of natural deposits
Sodium (ppm) 10 10 1 0.96 – 1.1 2014 No Runoff from fertilizer use; Leaching from septic tanks, sewage;
Nitrate [measured Erosion of natural deposits
as Nitrogen] (ppm)
Radioactive Contaminant
Alpha emitters (pCi/L) 0 15 2.6 1 – 2.9 2012 No Erosion of natural deposits
Uranium (pCi/L) 0 30 Erosion of natural deposits
2.3 1.3 – 2.8 2012 No
AL Typical Source
Contaminants MCLG 90th Sample # Samples
1.3 percentile Date Exceeding AL Corrosion of household plumbing systems; Erosion of natural
deposits
Copper - action 1.3 0.13 2012 0
level at consumer taps
(ppm)
Lead - action 0 15 0 2012 Corrosion of household plumbing systems; Erosion of natural
level at consumer taps 0 deposits
(ppb) Year Annual
Sampled Average Monthly Average MRDLG MRDL Typical Source
Contaminants Range
2014 0.7 Disinfection additive used to control microbes
Chlorine (ppm) 0.51 – 0.92 4 4
Term Definition
Unit Description
ug/L Number of micrograms of substance
ppm
ppb Parts Per Million. One ppm equals one milligrams per liter
(mg/L) or 1,000 times more than a ppb
pCi/L
Parts Per Billion. Some constituents in water are measured in
NA very small units. One ppb equals one micrograms per liter (μg/L)
ND
NR Picocurie Per Liter. It is defined as the quantity of radioactive
material in one liter which produces 2.222 nuclear disintegrations
per minute
Not Applicable
Not detected
NR: Monitoring not required, but recommended.
DETAILED INFORMATION ON CONTAMINANTS groundwater in the southwestern United States. While your drinking
Haloacetic Acids (HAA5) are a group of chemicals that are formed water meets USEPA’s standard for arsenic, it does contain low levels of
along with other disinfection-by-products when chlorine or other disin- arsenic. USEPA’s standard balances the current understanding of arse-
fectants used to control microbial contaminants in drinking water react nic’s possible health effects against the cost of removing arsenic from
with naturally occurring organic and inorganic matter in water. The regu- drinking water. USEPA continues to research the health effect of low
lated haloacetic acid compounds, known as HAA5, are monochloroacetic levels of arsenic which is a mineral known to cause cancer in humans
acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, monobromoacetic acid, at high concentrations and is linked to other health effects such as skin
and dibromoacetic acid. USEPA has established an MCL of 60 parts per damage and circulatory problems.
billion for HAA5. Compliance with the HAA5 standard is based on the
running annual average concentration. Barium occurs naturally at very low concentrations in our groundwater.
Total Trihalomethanes (TTHMs) are formed when chlorine combines Fluoride is an important naturally occurring mineral that helps to form
with naturally occurring organic material in water. Since the level of healthy teeth and bones. A concentration of 1 ppm is considered optimum.
organic matter in our groundwater is extremely low, these compounds are At concentrations above 2 ppm, fluoride can cause mild discoloration of
found at very low concentrations. The compounds which make up the teeth, and exposure at above the MCL of 4 ppm can cause both severe dis-
TTHMs include bromodichloromethane, bromoform, chlorodibromo- coloration of teeth and over many years of exposure, bone disease.
methane, and chloroform. Compliance with the TTHM standard is based Nitrate is a form of nitrogen and an important plant nutrient. Nitrate
on the running annual average concentration. in drinking water at levels above 10 ppm is a health risk for infants less
Arsenic is a naturally occurring substance commonly found in than six months of age. High nitrate levels in drinking water can cause
blue baby syndrome. Nitrate levels may rise quickly for short periods of
See WATER, Page 11