Page 55 - 2018_Jour_85-1_Societal-Issues
P. 55
Schools and Societal Issues 55
Summary of Research Findings
Participants confirmed that their perceptions of their ability and willingness to
participate in traditional post-observation conversations were positive. They believed in
self-reflecting and strengthening practice to meet students’ needs and thought that most of
their colleagues would agree with these concepts. Participants agreed that effective feedback
during traditional post-observation conversations would make it easier to self-reflect
and strengthen practice. Obstacles to the success of such conversations were perceived
by participants as (a) unavailability of time to hold the conversation, (b) conversations
not taking place immediately, (c) ineffective feedback provided by the observer, and (d)
conversations that were not positive. They perceived that the SOAP format improved
traditional methods in the following ways: feedback was effective, the conversation was
immediate, and the conversation was positive.
Participants’ responses were favorable to the researcher’s suggestions on improving
practice that were given in SOAP-formatted post-observation conversations. Student
achievement motivated teachers to self-reflect and strengthen practice through these
conversations to meet goals they set for their students. They perceived change to be
anywhere from easy to difficult but, due to their strong attitude and subjective norms, they
had a stronger perception of behavior control.
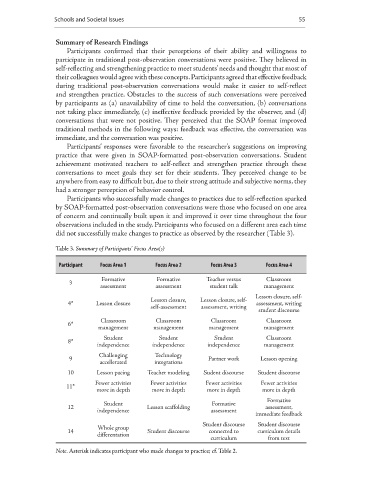
Participants who successfully made changes to practices due to self-reflection sparked
by SOAP-formatted post-observation conversations were those who focused on one area
of concern and continually built upon it and improved it over time throughout the four
observations included in the study. Participants who focused on a different area each time
did not successfully make changes to practice as observed by the researcher (Table 3).
Table 3. Summary of Participants’ Focus Area(s)
Participant Focus Area 1 Focus Area 2 Focus Area 3 Focus Area 4
Formative Formative Teacher versus Classroom
3
assessment assessment student talk management
Lesson closure, self-
Lesson closure, Lesson closure, self-
4* Lesson closure assessment, writing
self-assessment assessment, writing
student discourse
Classroom Classroom Classroom Classroom
6*
management management management management
Student Student Student Classroom
8*
independence independence independence management
Challenging Technology
9 Partner work Lesson opening
accellerated integrations
10 Lesson pacing Teacher modeling Sudent discourse Student discourse
Fewer activities Fewer activities Fewer activities Fewer activities
11*
more in depth more in depth more in depth more in depth
Formative
Student Formative
12 Lesson scaffolding assessment,
independence assessment
immediate feedback
Student discourse Student discourse
Whole group
14 Student discourse connected to curriculum details
differentation
curriculum from text
Note. Asterisk indicates participant who made changes to practice; cf. Table 2.