Page 400 - The ROV Manual - A User Guide for Remotely Operated Vehicles 2nd edition
P. 400
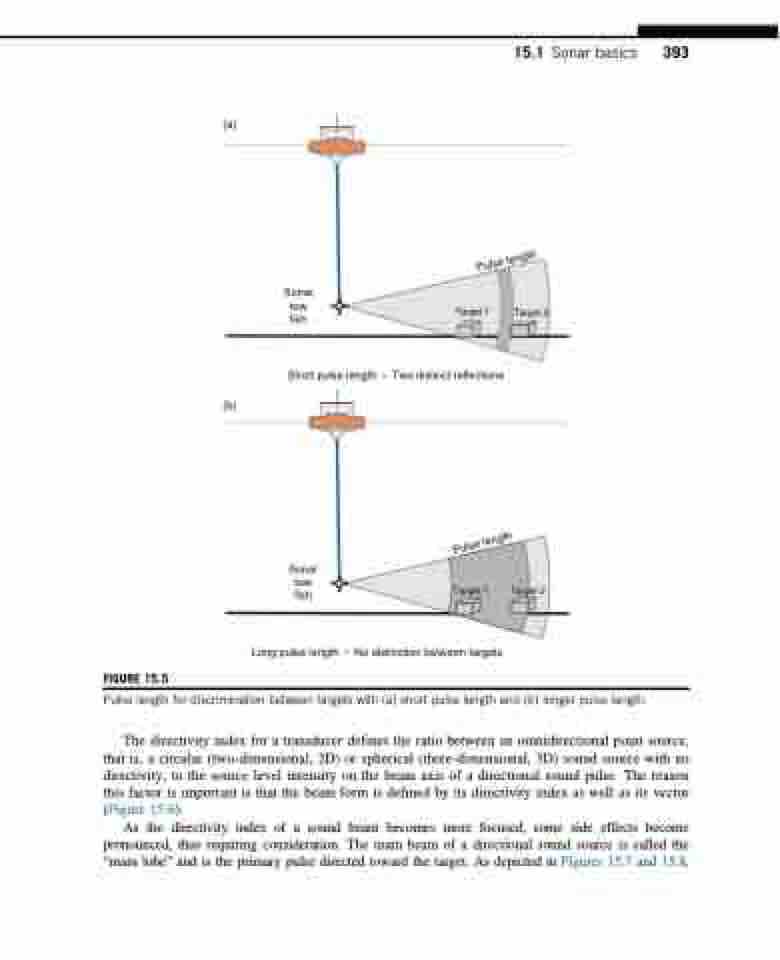
(a)
15.1 Sonar basics 393
(b)
Sonar tow fish
Short pulse length
Target 1
Two distinct reflections
Target 2
FIGURE 15.5
Sonar tow fish
Long pulse length
Target 1
No distinction between targets
Target 2
Pulse length for discrimination between targets with (a) short pulse length and (b) longer pulse length.
The directivity index for a transducer defines the ratio between an omnidirectional point source, that is, a circular (two-dimensional, 2D) or spherical (three-dimensional, 3D) sound source with no directivity, to the source level intensity on the beam axis of a directional sound pulse. The reason this factor is important is that the beam form is defined by its directivity index as well as its vector (Figure 15.6).
As the directivity index of a sound beam becomes more focused, some side effects become pronounced, thus requiring consideration. The main beam of a directional sound source is called the “main lobe” and is the primary pulse directed toward the target. As depicted in Figures 15.7 and 15.8,
Pulse length
Pulse length