Page 503 - The ROV Manual - A User Guide for Remotely Operated Vehicles 2nd edition
P. 503
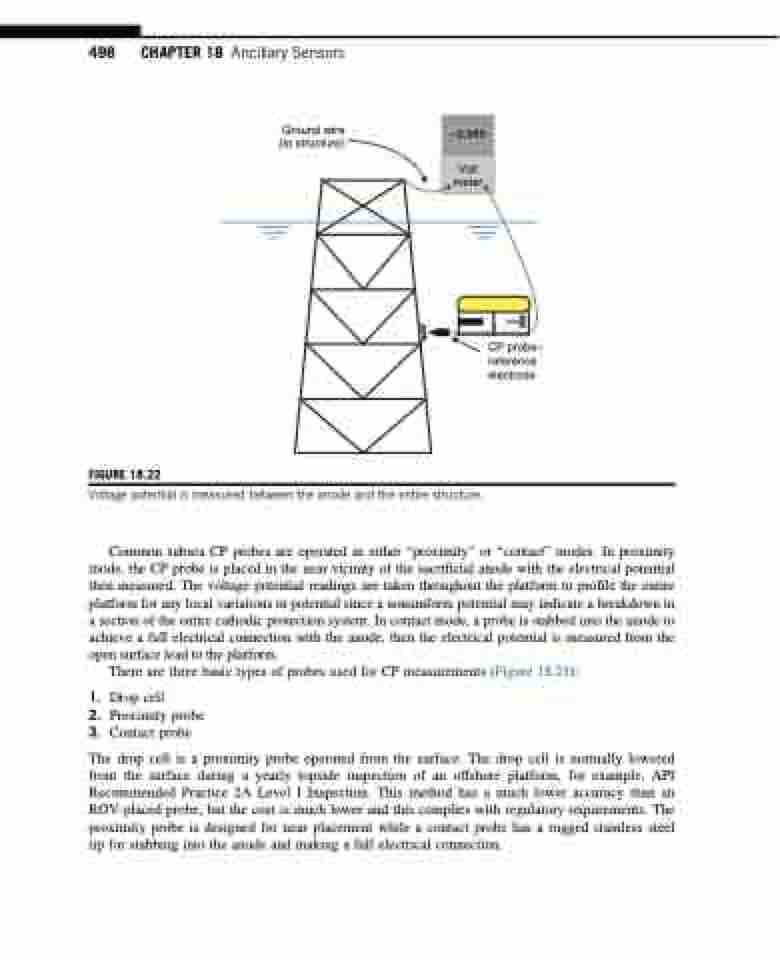
498 CHAPTER 18 Ancillary Sensors
–0.985
Volt meter
Ground wire (to structure)
FIGURE 18.22
CP probe– reference electrode
Voltage potential is measured between the anode and the entire structure.
Common subsea CP probes are operated in either “proximity” or “contact” modes. In proximity mode, the CP probe is placed in the near vicinity of the sacrificial anode with the electrical potential then measured. The voltage potential readings are taken throughout the platform to profile the entire platform for any local variations in potential since a nonuniform potential may indicate a breakdown in a section of the entire cathodic protection system. In contact mode, a probe is stabbed into the anode to achieve a full electrical connection with the anode, then the electrical potential is measured from the open surface lead to the platform.
There are three basic types of probes used for CP measurements (Figure 18.23):
1. Drop cell
2. Proximity probe 3. Contact probe
The drop cell is a proximity probe operated from the surface. The drop cell is normally lowered from the surface during a yearly topside inspection of an offshore platform, for example, API Recommended Practice 2A Level I Inspection. This method has a much lower accuracy than an ROV-placed probe, but the cost is much lower and this complies with regulatory requirements. The proximity probe is designed for near placement while a contact probe has a rugged stainless steel tip for stabbing into the anode and making a full electrical connection.