Page 23 - The Insurance Times September 2025
P. 23
Impact of RBC on Life Insurer in Nepal off is thinner protection against any adversities or
shocks.
Nepal's insurance regulator officially introduced the Risk-
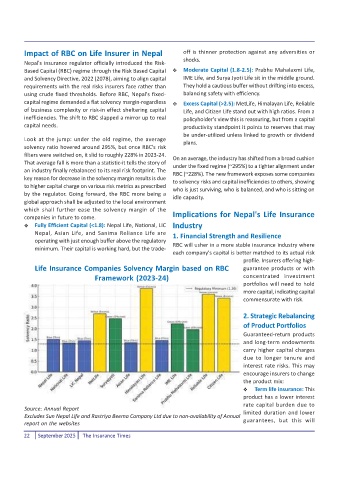
Based Capital (RBC) regime through the Risk Based Capital Moderate Capital (1.8-2.5): Prabhu Mahalaxmi Life,
and Solvency Directive, 2022 (2078), aiming to align capital IME Life, and Surya Jyoti Life sit in the middle ground.
requirements with the real risks insurers face rather than They hold a cautious buffer without drifting into excess,
using crude fixed thresholds. Before RBC, Nepal's fixed- balancing safety with efficiency.
capital regime demanded a flat solvency margin-regardless Excess Capital (>2.5): MetLife, Himalayan Life, Reliable
of business complexity or risk-in effect sheltering capital Life, and Citizen Life stand out with high ratios. From a
inefficiencies. The shift to RBC slapped a mirror up to real policyholder's view this is reassuring, but from a capital
capital needs. productivity standpoint it points to reserves that may
be under-utilized unless linked to growth or dividend
Look at the jump: under the old regime, the average
plans.
solvency ratio hovered around 295%, but once RBC's risk
filters were switched on, it slid to roughly 228% in 2023-24.
On an average, the industry has shifted from a broad cushion
That average fall is more than a statistic-it tells the story of
under the fixed regime (~295%) to a tighter alignment under
an industry finally rebalanced to its real risk footprint. The
RBC (~228%). The new framework exposes some companies
key reason for decrease in the solvency margin results is due
to solvency risks and capital inefficiencies to others, showing
to higher capital charge on various risk metrics as prescribed who is just surviving, who is balanced, and who is sitting on
by the regulator. Going forward, the RBC more being a
idle capacity.
global approach shall be adjusted to the local environment
which shall further ease the solvency margin of the
companies in future to come. Implications for Nepal's Life Insurance
Fully Efficient Capital (<1.8): Nepal Life, National, LIC Industry
Nepal, Asian Life, and Sanima Reliance Life are 1. Financial Strength and Resilience
operating with just enough buffer above the regulatory
RBC will usher in a more stable insurance industry where
minimum. Their capital is working hard, but the trade-
each company's capital is better matched to its actual risk
profile. Insurers offering high-
Life Insurance Companies Solvency Margin based on RBC guarantee products or with
Framework (2023-24) concentrated investment
portfolios will need to hold
more capital, indicating capital
commensurate with risk.
2. Strategic Rebalancing
of Product Portfolios
Guaranteed-return products
and long-term endowments
carry higher capital charges
due to longer tenure and
interest rate risks. This may
encourage insurers to change
the product mix:
Term life insurance: This
product has a lower interest
rate capital burden due to
Source: Annual Report
Excludes Sun Nepal Life and Rastriya Beema Company Ltd due to non-availability of Annual limited duration and lower
report on the websites guarantees, but this will
22 September 2025 The Insurance Times