Page 1083 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1083
CHAPTER 61 Dermatologic Pharmacology 1069
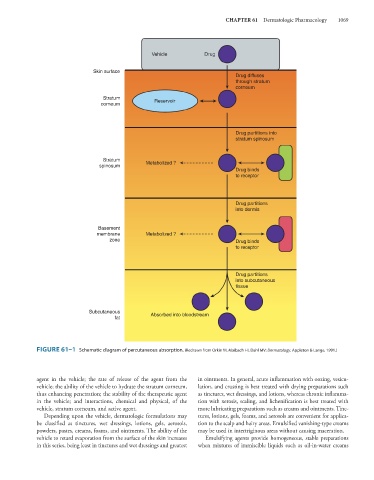
Vehicle Drug
Skin surface
Drug diffuses
through stratum
corneum
Stratum
corneum Reservoir
Drug partitions into
stratum spinosum
Stratum
spinosum Metabolized ?
Drug binds
to receptor
Drug partitions
into dermis
Basement
membrane Metabolized ?
zone Drug binds
to receptor
Drug partitions
into subcutaneous
tissue
Subcutaneous
fat Absorbed into bloodstream
FIGURE 61–1 Schematic diagram of percutaneous absorption. (Redrawn from Orkin M, Maibach HI, Dahl MV: Dermatology. Appleton & Lange, 1991.)
agent in the vehicle; the rate of release of the agent from the in ointments. In general, acute inflammation with oozing, vesicu-
vehicle; the ability of the vehicle to hydrate the stratum corneum, lation, and crusting is best treated with drying preparations such
thus enhancing penetration; the stability of the therapeutic agent as tinctures, wet dressings, and lotions, whereas chronic inflamma-
in the vehicle; and interactions, chemical and physical, of the tion with xerosis, scaling, and lichenification is best treated with
vehicle, stratum corneum, and active agent. more lubricating preparations such as creams and ointments. Tinc-
Depending upon the vehicle, dermatologic formulations may tures, lotions, gels, foams, and aerosols are convenient for applica-
be classified as tinctures, wet dressings, lotions, gels, aerosols, tion to the scalp and hairy areas. Emulsified vanishing-type creams
powders, pastes, creams, foams, and ointments. The ability of the may be used in intertriginous areas without causing maceration.
vehicle to retard evaporation from the surface of the skin increases Emulsifying agents provide homogeneous, stable preparations
in this series, being least in tinctures and wet dressings and greatest when mixtures of immiscible liquids such as oil-in-water creams